1. Both cilium and flagellum emerges from centriole like structure which is called
a) Basal granules
b) Basal bodies
c) Basal lamina
d) Basal ganglion
Explanation: Basal bodies
2.The name ‘chromatin’ was given by
a) Robert Brown
b) Fleming
c) Schwann
d) Ramchandran
Explanation: Fleming
3. The outer membrane of nucleus remains continuous with which cell organelle
a) ER
b) Golgi body
c) Lysosome
d) All of these
Explanation: ER
4. The perinuclear space is about
a) 1–5 nm
b) 5–10 nm
c) 10–50 nm
d) > 100 nm
Explanation: 10–50 nm
5. The following cells are without nucleus
a) Erythrocytes of many mammals
b) Sieve tube cells of vascular plant
c) Bacterial cell
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
6. The site of active ribosomal RNA synthesis is
a) Nucleolus
b) Mitochondria
c) Cytoplasm
d) All of these
Explanation: Nucleolus
7. Chromatin contains
a) DNA
b) Basic protein histone
c) Some non-histone protein and RNA
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
8. How long a DNA is distributed in our forty six chromosomes?
a) 1 metre
b) 3 metre
c) 2 metre
d) 4 metre
Explanation: 2 metre
9. Based on the position of centromere, the chromosomes are classified into how many types?
a) 1
b) 3
c) 2
d) 4
Explanation: 4 types
10. Identify A, B, C and D given in the figure. 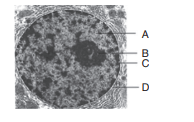
a) A–Nucleoplasm, B–Nucleolus, C–Nuclear pore, D–Nuclear membrane
b) A–Nucleolus, B–Nucleoplasm, C–Nuclear membrane, D–Nuclear pore
c) A–Nuclear pore, B–Nuclear membrane, C–Nucleoplasm, D–Nucleolus
d) A–Nuclear membrane, B–Nucleoplasm, C–Nuclear pore, D–Nuclear membrane
Explanation: A–Nucleoplasm, B–Nucleolus, C–Nuclear pore, D–Nuclear membrane