1. Which of the following wall is capable of growth in a plant cell?
a) Primary wall
b) Secondary wall
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) Middle lamella
Explanation: Primary wall is capable of growth in a plant cell
2. What is the component of middle lamella that puts the different binds neighbouring cells together?
a) Calcium phosphate
b) Sodium pectate
c) Calcium pectate
d) Sodium phosphate
Explanation: Calcium pectate
3. A structure that is traversing the middle lamella and connecting the cytoplasm of neighbouring
cells is called
a) Primary wall junction
b) Plasmodesmata
c) Desmosomes
d) Secondary wall
Explanation: A structure that is traversing the middle lamella and connecting the cytoplasm of neighbouring cells is called Plasmodesmata.
4. Identify the A, B, C, D and E in this figure. 
a) A–Nuclear pore, B–Nucleus, C–Ribosome, D–Smooth endoplasmic reticulum, E–Rough
endoplasmic reticulum
b) A–Rough endoplasmic reticulum, B–Nuclear pore, C–Ribosome, D–Smooth endoplasmic
reticulum, E–Nucleus
c) A–Ribosome, B–Nuclear pore, C–Nucleus, D–Smooth endoplasmireticulum, E–Rough
endoplasmic reticulum
d) A–Nucleus, B–Nuclear pore, C–Rough endoplasmic reticulum, D–Ribosome, E–Smooth
endoplasmic reticulum
Explanation: A–Nucleus, B–Nuclear pore, C–Rough endoplasmic reticulum, D–Ribosome, E–Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
5. How many of the following are not included in endomembrane system?
Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi complex, Lysosome, Mitochondria, Chloroplast, Vacuoles,
Peroxisomes
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
Explanation: 3
6. What is the network of tiny tubular structures scattered in cytoplasm as seen from electron
microscope?
a) Golgi complex
b) Microtubule
c) Endoplasmic reticulum
d) Mitochondria
Explanation: Endoplasmic reticulum
7. What indicates A in the figure?
a) Cisternae
b) Nuclear pore
c) Crista
d) Thylakoid
Explanation: Cisternae
8. Which side in a cell does luminal and extra luminal compartments are situated respectively?
a) Cytoplasm, inside ER
b) Inside ER, cytoplasm
c) cytoplasm, plasma membrane
d) Nucleus, cytoplasm
Explanation: Inside ER, cytoplasm
9. Rough endoplasmic reticulum is called so due to the presence of
a) Lysosome
b) Golgi granules
c) Ribosomes
d) Protein granules
Explanation: Rough endoplasmic reticulum is called so due to the presence of Ribosomes
10. RER is frequently seen in cells associated with frequent synthesis and secretion of
a) Lipid
b) Glucose
c) Protein
d) All of these
Explanation: Protein
11. SER is frequently associated with the synthesis of
a) Lipid
b) Glucose
c) Protein
d) All of these
Explanation: SER is frequently associated with the synthesis of Lipid
12. What is the diameter of cisternae?
a) 0.5 to 1 μm
b) 0.5 to 1 mm
c) 0.5 to 2 μm
d) 5 to 11 μm
Explanation: 0.5 to 1 μm
13. Cis and trans face of golgi body are ____ and ____ respectively.
a) Convex, Concave
b) Concave, Convex
c) Convex, Convex
d) Concave, Concave
Explanation: Cis and trans face of golgi body are convex and concave respectively.
14. Which face of golgi apparatus receives the materials packaged in the form of vesicles from
the ER?
a) Cis
b) Trans
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
Explanation: Cis
15. Golgi apparatus is an important site for the formation of
a) Protein and lipids
b) Glycoproteins and glycolipids
c) Carbohydrates and proteins
d) Glucose and lipids
Explanation: Golgi apparatus is an important site for the formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids
16. Which structure is formed by the process of packaging in golgi apparatus?
a) Ribosomes
b) Protein granules
c) Lysosomes
d) Centrosomes
Explanation: Lysosomes
17. Which of the following are not hydrolytic enzyme?
a) Lipase
b) Proteases
c) Carbohydrases
d) Ligases
Explanation: Ligases are not hydrolytic enzyme
18. Hydrolytic enzymes are activated at _______ pH.
a) Acidic
b) Neutral
c) 0 basic
d) All of these
Explanation: Hydrolytic enzymes are activated at acidic pH.
19. Which of the following cannot be digested by hydrolytic enzymes?
a) DNA
b) Immunoglobulins
c) Glucose
d) Insulin
Explanation: Glucose
20. Which of the following are not the contents of vacuole?
a) Water
b) Enzymes
c) Sap
d) Excretory products
Explanation: Enzymes
21. Which of the following is correct about vacoule?
a) Vacuole contain water sap, excretory product and other material not useful for the cell .
b) In plant cell the vacuole can occupy up to 90 per cent of the volume of the cell.
c) The vacuole is bounded by tonoplast.
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
22. Tonoplast membrane is important for
a) Transporting ions along concentration gradient.
b) Transporting ions against concentration gradient.
c) Providing rigidity to structure
d) All of these
Explanation: Tonoplast membrane is important for transporting ions against concentration gradient
23. The contractile vacuole present in amoeba is useful for
a) Ingestion
b) Locomotion
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) Excretion
Explanation: Excretion
24. The amount or number of mitochondria in a cell depends on
a) Anatomical structure of cell
b) Size of the cell
c) Colour and contour of the cell
d) Physiological activity of cell
Explanation: The amount or number of mitochondria in a cell depends on physiological activity of cell
25. What is the main function of cristae?
a) To hold the vesicles formed
b) Increase the surface area
c) Increase the density of organelle
d) All of these
Explanation: Increase the surface area
26. What kind of ribosome is seen in mitochondria?
a) 80S
b) 70S
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
Explanation: 70S
27. How is a new mitochondria formed by the pre-existing ones?
a) Mitosis
b) Fission
c) Conjugation
d) Budding
Explanation: Fission
28. What does a chloroplast contain?
a) Chlorophyll
b) Carotenoid
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) Anthocyanin
Explanation: Both (a) and (b)
29. Select the incorrect pair from the following:
a) Leucoplast-Carotene
b) Amyloplast-Starch
c) Elaioplast-Oils
d) Aleuroplasts–Proteins
Explanation: "Leucoplast-Carotene". This is incorrect
30. In 30S and 40S ribosomes, ‘S’ stands for
a) Sub-unit
b) Svedberg’s unit
c) Single unit
d) Size
Explanation: Svedberg’s unit
31. Identify A, B, C, D and E in the given figure 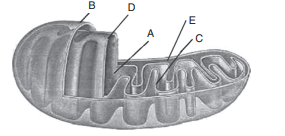
a) A–Matrix, B–Outer membrane, C–Crista, D–Inner membrane, E–Inner-membrane space
b) A–Crista, B–Outer membrane, C–Inner-membrane space, D–Inner membrane, E–Matrix
c) A–Matrix, B–Inner membrane, C–Inner-membrane space, D–Crista, E–Outer membrane
d) A–Inner-membrane space, B–Outer membrane, C–Matrix, D–Crista, E–Inner membrane
Explanation: A–Matrix, B–Outer membrane, C–Crista, D–Inner membrane, E–Inner-membrane space
32. What kind of ribosome is present in mitochondria?
a) 70S
b) 80S
c) 40S
d) 60S
Explanation: 70S
33. Plastids are found in
a) All plant cells
b) All animal cells
c) Euglenoids
d) Both (a) and (c)
Explanation: Both (a) and (c)
34. Based on the type of pigments, the plastid can be classified into how many types?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Explanation: 3
35.Which of the following is a type of plastid?
a) Chloroplast
b) Chromoplast
c) Leucoplast
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
36. Select the correct matching:
Column I Column II
(Type of leucoplast) (Stored food)
A. Amyloplast 1. Oil and fat
B. Elaioplast 2. Protein
C. Aleuroplasts 3. Carbohydrate
a) A–3, B–1, C–2
b) A–1, B–2, C–3
c) A–3, B–2, C–1
d) A–2, B–3, C–1
Explanation: A–3, B–1, C–2
37. Select the incorrect statement:
a) The chloroplast contains chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments
b) Chromoplast contains water soluble carotenoid pigments like carotene, xanthophylls.
c) Plastid is easily observed under microscope.
d) Chloroplast is a double membrane bound organelle.
Explanation: "Chromoplast contains water soluble carotenoid pigments like carotene, xanthophylls". This is incorrect statement.
38. The number of chloroplast in alga chlamydomonas is
a) 2
b) 1
c) 20 to 40
d) 5 to 10
Explanation: The number of chloroplast in alga chlamydomonas is 1
39. Identify A to F in the given figure. 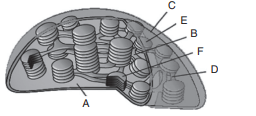
a) A–Outer membrane, B–Thylakoid, C–Stroma lamella, D–Inner membrane, E–Granum,
F–Stroma
b) A–Thylakoid, B–Outer membrane, C–Stroma lamella, D–Inner membrane, E–Stroma,
F–Granum
c) A–Stroma, B–Granum, C–Outer membrane, D–Stroma lamella, E–Inner membrane,
F–Thylakoid
d) A–Inner membrane, B–Thylakoid, C–Stroma lamella, D–Outer membrane, E–Stroma,
F–Granum
Explanation: A–Stroma, B–Granum, C–Outer membrane, D–Stroma lamella, E–Inner membrane, F–Thylakoid
40. Number of chloroplast present in a mesophyll cell
a) 5–10
b) 10–15
c) 20–40
d) > 100
Explanation: 20–40
41. Chlorophyll pigments are present in
a) Thylakoid
b) Stroma
c) Outer membrane
d) Inner membrane
Explanation: Chlorophyll pigments are present in thylakoid
42. Ribosomes are the granular structure first observed under the electron microscope as dense
particle by which scientist
a) Robert Brown (1831)
b) George Palade (1953)
c) Camillo Golgi (1898)
d) Singer and Nicolson (1972)
Explanation: George Palade (1953)
43. The types of ribosome present in eukaryote cell is
a) 70S
b) 80S
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
Explanation: Both (a) and (b)
44. An elaborate network of filamentous proteinaceous structures present in the cytoplasm is
collectively known as
a) Cilia
b) Flagella
c) Cytoskeleton
d) ER
Explanation: An elaborate network of filamentous proteinaceous structures present in the cytoplasm is collectively known as Cytoskeleton
45. Cytoskeleton helps in
a) Mechanical support to cell
b) Providing mobility to cell
c) Maintenance of shape of cell
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
46. The central part of the proximal region of the centriole is also proteinaceous and is called
a) Spokes
b) Doublet
c) Hub
d) Linkers
Explanation: The central part of the proximal region of the centriole is also proteinaceous and is called Hub
47. Find out the incorrect statement:
a) Centrioles forms basal bodies of cilia or flagella.
b) Centriole gives rise to spindle fibres at the time of cell division in animal cell.
c) Centrosome is an organelle usually containing two cylindrical structures called centrioles.
d) Peripheral fibril of centriole is doublet.
Explanation: "Peripheral fibril of centriole is doublet". This is incorrect.
48. Identify A, B, C, D, E and F given in the figure. 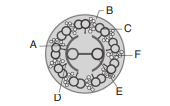
a) A–Interdoublet bridge, B–Peripheral microtubules (doublets), C–Central microtubule, D–
Plasma membrane, E–Central bridge, F–Radial spoke
b) A–Central sheath, B–Radial spoke, C–Interdoublet bridge, D–Central microtubule, E–
Plasma membrane, F–Peripheral microtubules (doublets)
c) A–Central sheath, B–Plasma membrane, C–Peripheral microtubules (doublets), D–Radial
spoke, E–Central microtubule, F–Interdoublet bridge
d) A–Plasma membrane, B–Radial spoke, C–Peripheral microtubules (doublets), D–Central
sheath, E–Central microtubule, F–Interdoublet bridge
Explanation: A–Central sheath, B–Plasma membrane, C–Peripheral microtubules (doublets), D–Radial spoke, E–Central microtubule, F–Interdoublet bridge
49. Select the incorrect statement:
a) Cilia and flagella are hair-like outgrowths of the cell membrane.
b) Cilia causes the movement of either the cell or the surrounding medium.
c) Bacterial flagella are structurally similar to eukaryotic flagella.
d) Flagella is responsible for cell movement.
Explanation: "Bacterial flagella are structurally similar to eukaryotic flagella". This is incorrect statement.
50. Which of the following is true about the internal structure of axoneme?
a) Central sheath is connected to one of the tubule of each peripheral doublets by a radial
spoke
b) Axoneme is not covered by plasma membrane at all.
c) Then are only and radial spokes are found.
d) Peripheral doublets are not connected with each other.
Explanation: Central sheath is connected to one of the tubule of each peripheral doublets by a radial spoke
51. Both cilium and flagellum emerges from centriole like structure which is called
a) Basal granules
b) Basal bodies
c) Basal lamina
d) Basal ganglion
Explanation: Basal bodies
52.The name ‘chromatin’ was given by
a) Robert Brown
b) Fleming
c) Schwann
d) Ramchandran
Explanation: Fleming
53. The outer membrane of nucleus remains continuous with which cell organelle
a) ER
b) Golgi body
c) Lysosome
d) All of these
Explanation: ER
54. The perinuclear space is about
a) 1–5 nm
b) 5–10 nm
c) 10–50 nm
d) > 100 nm
Explanation: 10–50 nm
55. The following cells are without nucleus
a) Erythrocytes of many mammals
b) Sieve tube cells of vascular plant
c) Bacterial cell
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
56. The site of active ribosomal RNA synthesis is
a) Nucleolus
b) Mitochondria
c) Cytoplasm
d) All of these
Explanation: Nucleolus
57. Chromatin contains
a) DNA
b) Basic protein histone
c) Some non-histone protein and RNA
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
58. How long a DNA is distributed in our forty six chromosomes?
a) 1 metre
b) 3 metre
c) 2 metre
d) 4 metre
Explanation: 2 metre
59. Based on the position of centromere, the chromosomes are classified into how many types?
a) 1
b) 3
c) 2
d) 4
Explanation: 4 types
60. Identify A, B, C and D given in the figure. 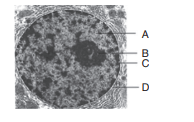
a) A–Nucleoplasm, B–Nucleolus, C–Nuclear pore, D–Nuclear membrane
b) A–Nucleolus, B–Nucleoplasm, C–Nuclear membrane, D–Nuclear pore
c) A–Nuclear pore, B–Nuclear membrane, C–Nucleoplasm, D–Nucleolus
d) A–Nuclear membrane, B–Nucleoplasm, C–Nuclear pore, D–Nuclear membrane
Explanation: A–Nucleoplasm, B–Nucleolus, C–Nuclear pore, D–Nuclear membrane