1. \[CO_{2}\] dissociates from Carbaminohaemoglobin when
a) Low \[PO_{2}\] , low \[PCO_{2}\]
b) High \[PO_{2}\] , high \[PCO_{2}\]
c) Low \[PO_{2}\] , high \[PCO_{2}\]
d) High \[PO_{2}\] , low \[PCO_{2}\]
Explanation: High \[PO_{2}\], low \[PCO_{2}\]
2. Dissociation of oxyhaemoglobin can be promoted by
a) Low \[pCO_{2}\]
b) High \[pCO_{2}\]
c) Low body temperature
d) High blood pH
Explanation: Dissociation of oxyhaemoglobin can be promoted by high \[pCO_{2}\].
3. The enzyme essential for transport of \[CO_{2}\] as bicarbonate in blood is
a) Carboxypeptidase
b) Succinic dehydrogenase
c) Carbonic anhydrase
d) Thrombokinase
Explanation: Carbonic anhydrase
4. What is correct about human respiration?
a) About 90 per cent of \[CO_{2}\] is carried by haemoglobin as carbaminohaemoglobin.
b) Neural signals from pneumotaxic centre of pons can increase the duration of inspiration.
c) Workers in grinding and stone breaking industries may suffer from lung fibrosis.
d) Cigarette smoking leads to inflammation of bronchi.
Explanation: "Workers in grinding and stone breaking industries may suffer from lung fibrosis". This one is correct about human respiration.
5. Choose the right sequential phenomena during the passage of \[CO_{2}\] from blood to tissues:
(P) Absorption of \[CO_{2}\] by blood.
(Q) Reaction of \[CO_{2}\] with water forming \[H_{2}CO_{3}\] inside RBCs and then \[HCO_3^-\] and \[H^{+}\] ions.
(R) Reaction of \[CO_{2}\] with water forming \[H_{2}CO_{3}\] inside plasma followed by conversion into H+
and \[HCO_3^-\] ions.
(S) Combination of H+ with haeme part of \[HbO_{2}\] to release \[O_{2}\].
(T) Combination of \[HCO_{3}\] with haeme part of \[HbO_{2}\] to form reduced haemoglobin and release
of \[O_{2}\] .
a) P, R, S
b) P, Q, T
c) P, Q, S
d) P, R, T
Explanation: P, Q, S
6. The transport of \[CO_{2}\] by the blood is primarily dependent on the
a) Solubility of \[CO_{2}\] in blood.
b) Presence of carbonic anhydrase in RBCs.
c) Ability of haemoglobin to bind and transport \[CO_{2}\]
d) Ability of other blood proteins.
Explanation: The transport of \[CO_{2}\] by the blood is primarily dependent on the presence of carbonic anhydrase in RBCs.
7. Pick the correct statement:
a) Contraction of internal intercostals muscles lifts up the ribs and sternum.
b) RBCs transport oxygen only.
c) Thoracic cavity is anatomically an air tight chamber.
d) Healthy man can inspire approximately 500 mL of air per minute.
Explanation: "Thoracic cavity is anatomically an air tight chamber". This is correct statement.
8.Respiratory rhythm centre is present in which part of brain?
a) Pons
b) Medulla oblongata
c) Cerebrum
d) Cerebellum
Explanation: Medulla oblongata
9. Pneumotaxic centre is present in
a) Pons
b) Medulla oblongata
c) Cerebrum
d) Cerebellum
Explanation: Pneumotaxic centre is present in pons.
10. Human beings have a significant ability to maintain and moderate the respiratory rhythm to
suit the demands of the body tissues. This is done by
a) Endocrine system
b) Neural system
c) Excretory system
d) All of these
Explanation: Neural system
11. (1) _________ sensitive area is situated adjacent to the rhythm centre which is highly
sensitive
to _________ (2) _and _ (3) _________ ions.
a) (1)–thermo, (2)–\[CO_{2}\] , (3)–hydroxide
b) (1)–chemo, (2)–\[O_{2}\] , (3)–hydroxide
c) (1)–thigmo, (2)–\[O_{2}\] , (3)–hydrogen
d) (1)–chemo, (2)–\[CO_{2}\] , (3)–hydrogen
Explanation: (1)–chemo, (2)–\[CO_{2}\] , (3)–hydrogen
12. All of the following factors play an important role in the regulation of respiratory rhythm
except
a) \[CO_{2}\]
b) \[H^{+}\] conc
c) \[O_{2}\]
d) none of these
Explanation: \[O_{2}\]
13. Select the incorrect statement from the following:
a) Neural signal from pneumotaxic centre can reduce the duration of inspiration.
b) The role of oxygen in the regulation of respiratory rhythm is quite significant
c) RBCs contain a very high concentration of the enzyme, carbonic anhydrase and minute
quantities of the same is present in the plasma too.
d) \[CO_{2}\] is carried by haemoglobin as carbamino-haemoglobin (about 20–25 per cent).
Explanation: "The role of oxygen in the regulation of respiratory rhythm is quite significant". This is incorrect statement.
14. Receptors associated with aortic and carotid artery can recognize changes in ______ and
_____ concentration and send necessary signal to _____ for remedial action.
a) \[O_{2}\] , \[CO_{2}\] , pneumotaxic
b) \[CO_{2}\] , H+, rhythm centre
c) \[CO_{2}\] , H+, apneustic centre
d) \[O_{2}\] , H+, pneumotaxic
Explanation: \[CO_{2}\] , H+, rhythm centre
15. Carbonic anhydrase is found in high concentration in
a) Leucocytes
b) Blood plasma
c) Erythrocytes
d) Lymphocytes
Explanation: Erythrocytes
16. The controlling centre of normal breathing in mammals lies in
a) Cerebrum
b) Cerebellum
c) Midbrain
d) Medulla oblongata
Explanation: Medulla oblongata
17. Number of RBCs per unit volume of blood is likely to be higher in a person living at high
altitudes, because
a) Air is clean and unpolluted
b) More sunshine is available
c) Air is less dense
d) Vegetation gives out more \[O_{2}\]
Explanation: Air is less dense
18. Wheezing sound is produced in
a) Asthma
b) Emphysema
c) Silicosis
d) Pneumonia
Explanation: Wheezing sound is produced in asthma .
19.Major cause of emphysema is
a) Cigarette smoking
b) Allergy
c) Wine consumption
d) Viral infection
Explanation: Cigarette smoking
20. Match the column:
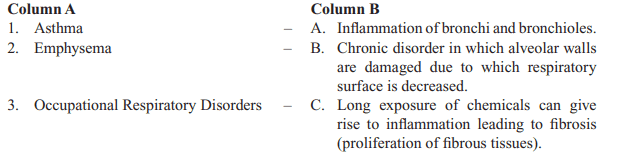
a) 1-A, 2-B, 3-C
b) 1-B, 2-A, 3-C
c) 1-C, 2-A, 3-B
d) 1-C, 2-B, 3-A
Explanation: 1-A, 2-B, 3-C
21. Emphysema is a
a) Cardiovascular disease
b) Pulmonary disease
c) Renal disease
d) Pain in lungs
Explanation: Emphysema is a Pulmonary disease.
22. Which of the following is incorrect about occupational respiratory disorder?
a) It occur in some industries, especially those involving grinding or stone-breaking.
b) Long exposure in such industries leading to fibrosis (proliferation of fibrous tissues).
c) Workers in such industries can be protected from these disorders by wearing protective
masks.
d) It is an allergic disease always.
Explanation: "It is an allergic disease always". This one is incorrect about occupational respiratory disorder.
23. Respiratory control centre lies in
a) Pons
b) Medulla oblongata
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) Cerebellum
Explanation: Both (a) and (b)
24. Two friends are eating together in a dining table. One of them suddenly starts coughing while
swallowing some food. This coughing would have been due to the improper movement of
a) Tongue
b) Epiglottis
c) Diaphragm
d) Neck
Explanation: Epiglottis
25.Which one of the following is a possibility for most of us in regard to breathing, by making a
conscious effort?
a) One can breathe out air totally without oxygen.
b) One can breathe out air through Eustachian tubes by closing both the nose and the mouth.
c) One can consciously breathe out by moving the diaphragm alone without moving the ribs at all.
d) The lungs can be made fully empty by forcefully breathing out all air from them.
Explanation: One can consciously breathe out by moving the diaphragm alone without moving the ribs at all
26.Cartilaginous rings in respiratory passage are present in
a) Trachea only
b) Trachea and initial bronchioles only
c) Trachea, bronchi and initial bronchioles
d) None of these
Explanation: Trachea, bronchi and initial bronchioles
27. Which of the following represents a larger volume of air than that is normally found in the
resting tidal volume or a human lung?
a) Residual volume
b) Inspiratory reserve volume
c) Expiratory reserve volume
d) All the above
Explanation: All the above
28. Mark the correct statement from the following:
a) Tracheal rings are of hyaline cartilage.
b) Dorsal side of thoracic chamber is formed by sternum.
c) Expiration occurs when there is negative pressure in lungs.
d) All the above
Explanation: "Tracheal rings are of hyaline cartilage". This is correct statement.
29. 6000-8000 ml of air is the
a) Vital capacity of lungs
b) Volume of normal expiration per minute
c) Sum of IRV + ERV
d) Inspiratory capacity of lungs
Explanation: Volume of normal expiration per minute
30. The volume of air that remains in the lungs after normal expiration is
a) Residual volume
b) Vital capacity
c) Expiratory capacity
d) Functional residual capacity
Explanation: Functional residual capacity