1.Equation of a line which is parallel to the
line common to the pair of lines given by \[6x^2-xy-12y^2=0\] and
\[15x^2+14xy-8y^2=0\] and at a distance 7 from it is
a) 3x + 4y = 35
b) 5x – 2y = 7
c) 3x + 4y = – 35
d) Both a and c
Explanation:
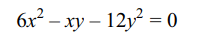
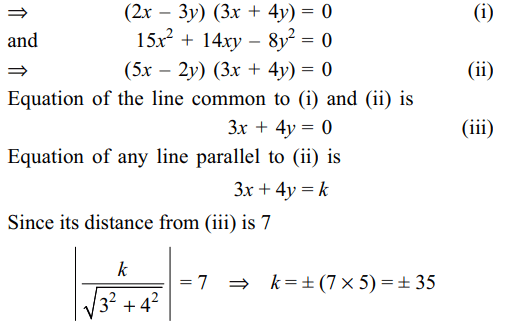
2. The lines joining the origin to the point
of intersection of \[3x^2+\lambda xy-4x+1=0\] and 2x + y – 1 = 0 are
at right angles for
a) \[\lambda=-4\]
b) \[\lambda=4\]
c) \[\lambda=7\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation: Equation of the lines joining the origin to the points of intersection of the given lines is
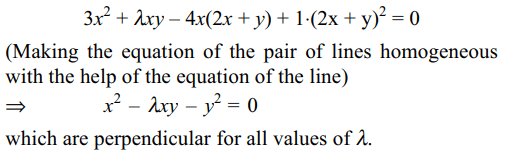
3. If \[x^2+2h xy+y^2=0\] represents the equations
of the straight lines through the origin which make an
angle \[\alpha\] with the straight line y + x = 0, then
a) \[\sec 2\alpha=h\]
b) \[\cos \alpha=\sqrt{\frac{1+h}{2h}}\]
c) \[\cot \alpha=\sqrt{\frac{h+1}{h-1}}\]
d) All of the Above
Explanation: Let equation of the lines given by x2 + 2hxy + y2 = 0 be y = m1x and y = m2x. Since these make an angle \[\alpha\] with y + x = 0 whose slope is –1,
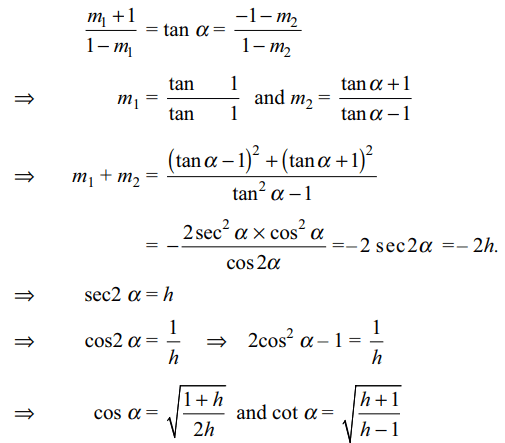
4. If the lines 2(sin a + sin b)x – 2(sin a – b)y = 3 and
2(cos a + cos b)x + 2cos(a – b)y = 5 are perpendicular,
then sin 2a + sin 2b is equal to
a) sin (a – b) – 2sin(a + b)
b) sin 2(a – b) – 2sin(a + b)
c) 2sin (a – b) – sin(a + b)
d) sin 2(a – b) – sin(a + b)
Explanation: Equation of the bisectors of the angles between the given lines is
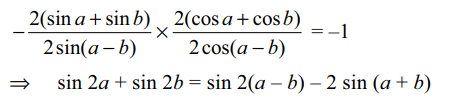
5. A(0, 0), B(2, 0), C(2, 2), D(0, 2) are the vertices of
a square ABCD. The square is rotated through an
angle of 30° in the anticlockwise direction so that
AB makes an angle of 30° with the positive direction
of x-axis. Equation of the diagonal BD in the new
position is
a) \[\left( \sqrt{3} +1\right)x +\left( \sqrt{2} -1\right) y = 3\]
b) \[\left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right)x +y=2\left( \sqrt{3} -1\right) \]
c) \[\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)x +y=2-\sqrt{3}\]
d) \[\left( \sqrt{2}-1 \right)x +\left( \sqrt{3}+1\right) y=3\]
Explanation: Let APQR be the new position of the square.
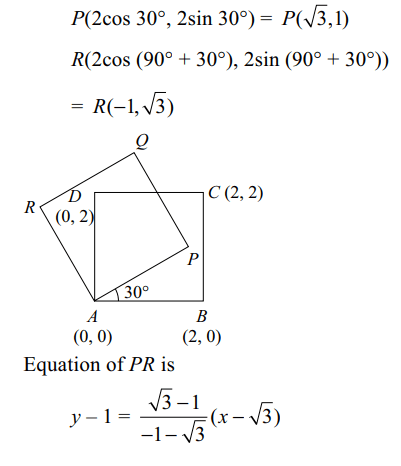
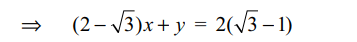
6. If the lines x + 2ay + a = 0, x + 3by + b = 0 and x +
4cy + c = 0 are concurrent, then a, b, c are in
a) A.P
b) G.P
c) H.P.
d) none of these
Explanation:
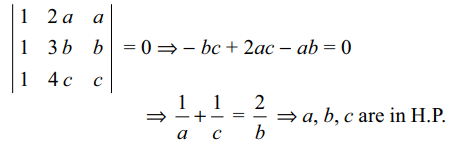
7. If the lines 2 (sin a + sin b) x - 2 sin (a - b) y = 3
and 2 (cos a + cos b) x + 2 cos (a - b)y = 5 are perpendicular,
then sin 2a + sin 2b is equal to
a) sin (a - b) - 2 sin (a + b)
b) sin 2 (a - b) - 2 sin (a + b)
c) 2 sin (a - b) - sin (a + b)
d) sin 2 (a - b) - sin (a + b)
Explanation:
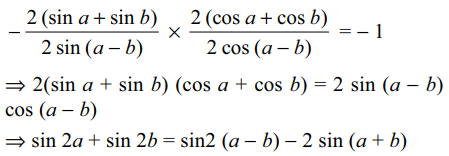
8. If \[p_{1},p_{2}\] denote the lengths of the perpendiculars
from the origin on the lines \[x\sec\alpha+\] y cosec \[\alpha=2a\]
and \[x\cos\alpha+y\sin\alpha=a\cos 2\alpha\] respectively, then
\[\left(\frac{p_{1}}{p_{2}}+\frac{p_{2}}{p_{1}}\right)^2\]
is equal to
a) \[4\sin^2 4\alpha\]
b) \[4\cos^2 4\alpha\]
c) 4 cosec2 \[4\alpha\]
d) \[4\sec^2 4\alpha\]
Explanation:

9. The locus of the point of intersection of the lines
\[x\sin \theta+\left(1-\cos\theta\right)y=a\sin\theta\]
and \[x\sin \theta-\left(1+\cos\theta\right)y+a\sin\theta=0\]
is
a) \[x^2-y^2=a^2\]
b) \[x^2+y^2=a^2\]
c) \[y^2=ax\]
d) none of these
Explanation:

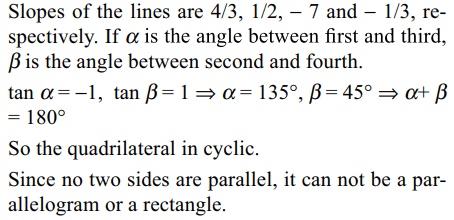
10. The straight lines 4x - 3y - 5 = 0, x - 2y - 10 = 0, 7x
+ y - 40 = 0 and x + 3y + 10 = 0 form the sides of a
a) quadrilateral
b) cyclic quadrilateral
c) rectangle
d) parallelogram
Explanation: