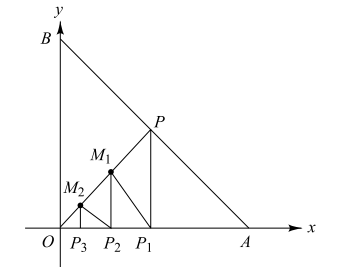
1. The line x + y = 1 meets x-axis at A and
y-axis at B. P is the mid-point of AB. \[P_{1}\] is the
foot of the perpendicular from P to OA; M1 is that from \[P_{1}\]
to OP; \[P_{2}\] is that from \[M_{1}\] to OA; \[M_{2}\] is that from \[P_{2}\] to OP;
\[P_{3}\] is that from \[M_{2}\] to OA and so on. If \[P_{n}\] denotes the nth
foot of the perpendicular on OA from \[M_{n-1}\] , then \[OP_{n}\] =
a) 1/2
b) \[1/2^{n}\]
c) \[1/2^{n/2}\]
d) \[1/\sqrt{2}\]
Explanation: x + y = 1 meets x-axis at A(1, 0) and y-axis at B(0, 1)
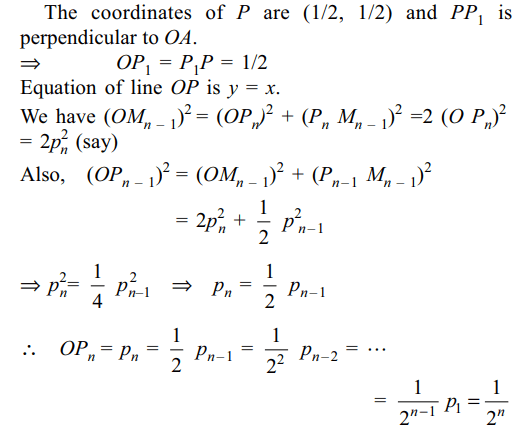
2. The line x + y = a, meets the axis of x and
y at A and B respectively. A triangle AMN is inscribed in
the triangle OAB, O being the origin, with right angle at N.
M and N lie respectively on OB and AB. If the area of the
triangle AMN is 3/8 of the area of the triangle OAB, then
AN/BN is equal to
a) 3
b) 1/3
c) 2
d) 1/2
Explanation:


3.The point (4, 1) undergoes the following
transformation successively.
(i) reflection about the line y = x.
(ii) translation through a distance 2 units along the
positive direction of x-axis.
(iii) rotation through an angle \[\pi\]/4 about the origin in the
anticlockwise direction.
(iv) reflection about x = 0
The final position of the given point is
a) \[\left(1/\sqrt{2},7/2\right)\]
b) \[\left(1/2,7/\sqrt{2}\right)\]
c) \[\left(1/\sqrt{2},7/\sqrt{2}\right)\]
d) (1/2, 7/2)
Explanation: Let B, C, D, E be the positions of the given point A(4, 1) after the transformations (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) successively
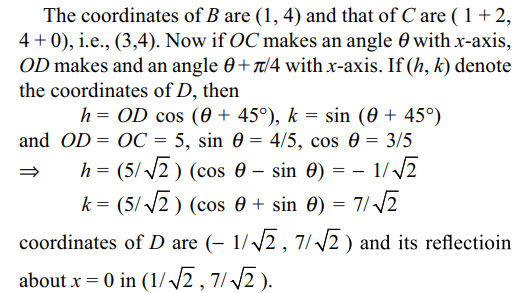
4. A line cuts the x-axis at A(7, 0) and the
y-axis at B(0, – 5). A variable line PQ is drawn perpendicular
to AB. Cutting the x-axis at P and the y-axis at Q.
If AQ and BP intersect at R, the locus of R is
a) \[x^{2}+y^{2}+7x-5y=0\]
b) \[x^{2}+y^{2}-7x+5y=0\]
c) \[5x-7y=35\]
d) none of these
Explanation: Let P(a, 0) and Q(0, b).
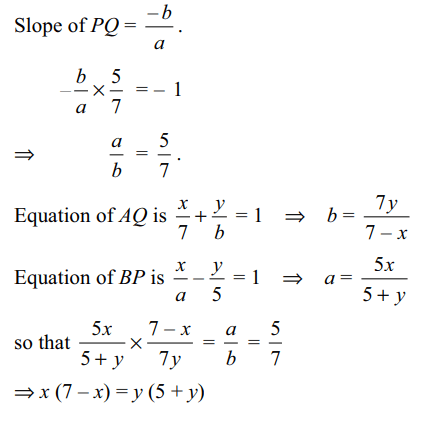

5. Equation of the line which bisects the
obtuse angle between the lines x – 2y + 4 = 0 and 4x
– 3y + 2 = 0 is
a) \[\left(4 + \sqrt{5}\right)x - \left(3 + 2 \sqrt{5}\right) y + 2 + 4 \sqrt{5} = 0\]
b) \[\left(4 - \sqrt{5}\right)x - \left(3 + 2 \sqrt{5}\right) y + 2 - 4 \sqrt{5} = 0\]
c) \[\left(4 - \sqrt{5}\right)x - \left(3 - 2 \sqrt{5}\right) y + 2 - 4 \sqrt{5} = 0\]
d) \[\left(4 + \sqrt{5}\right)x - \left(3 - 2 \sqrt{5}\right) y + 2 + 4 \sqrt{5} = 0\]
Explanation: Let us form a triangle with sides x – 2y + 4 = 0, 4x – 3y + 2 = 0 and x = 0. Coordinates of the vertices of this triangle are A(8/5, 14/5), B(0, 2/3) and C(0, 2).

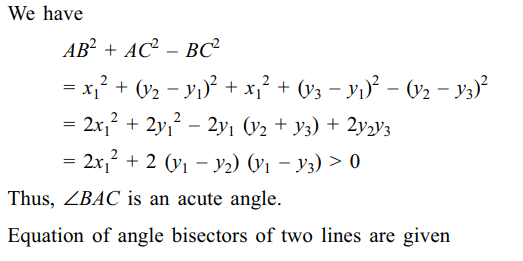

6. If the pairs of lines \[x^{2}+2xy+ay^{2}=0\] and
\[ax^{2}+2xy+y^{2}=0\] have exactly one line in common then
the joint equation of the other two lines is given by
a) \[3x^{2}+8xy-3y^{2}=0\]
b) \[3x^{2}+10xy+3y^{2}=0\]
c) \[y^{2}+2xy-3x^{2}=0\]
d) \[x^{2}+2xy-3y^{2}=0\]
Explanation: Let y = mx be a line common to the given pairs of lines, then

7. If the lines joining the origin to the intersection
of the line y = mx + 2 and the curve x2 + y2 = 1 are at
right angles, then
a) \[m^{2}=1\]
b) \[m^{2}=3\]
c) \[m^{2}=7\]
d) \[2m^{2}=1\]
Explanation: Joint equation of the lines joining the origin

8. Let PQR be a right angled isosceles triangle
right angled at P (2, 1). If the equation of the line QR is
2x + y = 3, then the equation representing the pair of lines
PQ and PR is
a) \[3x^{2}-3y^{2}+8xy+20x+10y+25=0\]
b) \[3x^{2}-3y^{2}+8xy-20x-10y+25=0\]
c) \[3x^{2}-3y^{2}+8xy+10x+15y+20=0\]
d) \[3x^{2}-3y^{2}-8xy-10x-15y-20=0\]
Explanation: Let the slopes of PQ and PR be m and

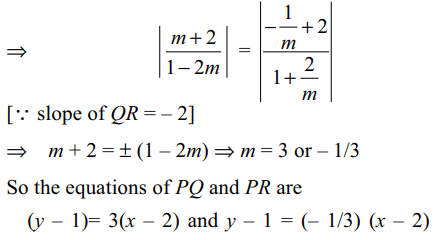
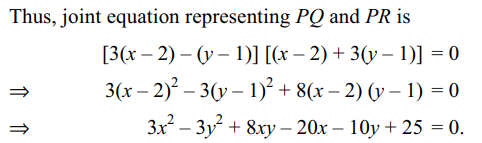
9. If \[\theta\] is an angle between the lines given
by the equation \[6x^{2}+5xy-4y^{2}+7x+13y-3=0\]
then equation of the line passing through the point of
intersection of these lines and making an angle \[\theta\] with the
positive x-axis is
a) 2x + 11y + 13 = 0
b) 11x – 2y + 13 = 0
c) 2x – 11y + 2 = 0
d) 11x + 2y – 11 = 0
Explanation: Writing the given equation as a quadratic in x


10. If one of the lines given by the equation
\[2x^{2}+axy+3y^{2}=0\] coincide with one of those given by
\[2x^{2}+bxy-3y^{2}=0\] and the other lines represented by them
be perpendicular, then
a) a = – 5, b = 1
b) a = 5, b = – 1
c) a = 5, b = 1
d) none of these
Explanation:

