1. The sample of x(n)={1,2,3,1} and h(n)={1,2,1,-1}, origin at 2, is 7.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: The input starts at n=0 and impulse at n=-1. So, output starts at n=0+(-1)=-1.
Output at is =4+4=1=7 samples. So, its true.
2. The convolution of x(n)={1,2,3,1} and h(n)={1,2,1,-1}, origin at 2, is?
a) {1,4,8,8,3,-2,-1}, origin at 4
b) {1,4,8,8,3,-2,1}, origin at 4
c) {1,3,8,8,3,-2,-1}, origin at 4
d) {1,4,8,3,-2,-1}, origin at 4
Explanation: Using tabular method:
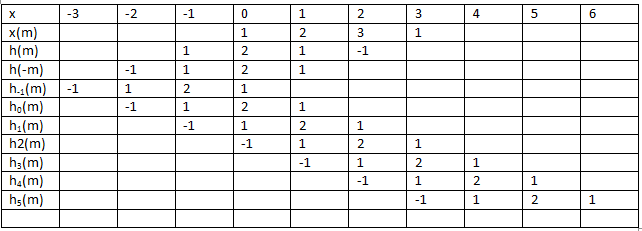
Hence, result is {1,4,8,8,3,-2,-1}, origin at 4.
3. The convolution sum is given by _____ equation.
a) x[n]*h[n] = \(∑_{k=-∞}^∞\) x[k]h[n-k]
b) x[n]*h[n] = \(∑_{k=-∞}^∞\) x[n]h[n-k]
c) x[n]*h[n] = \(∑_{k=-∞}^∞\) x[k]h[k]
d) x[n]*h[n] = \(∑_{k=-∞}^∞\) x[k]h[-k]
Explanation: By the definition of convolution sum we can write the equation as
x[n]*h[n] = ∑∞k=-∞ x[k]h[n-k]
4. The impulse response h (t) of an LTI system is given by e-2t.u(t) . What is the step response?
a) y(t) = 1⁄2 (1 – e-2t) u (t)
b) y(t) = 1⁄2 (1 – e-2t)
c) y(t) = (1- e-2t) u (t)
d) y(t) = 1⁄2 (e-2t) u (t)
Explanation: Given x (t) = u (t) and h (t) = e-2t.u(t). By using convolution integral
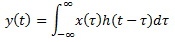
We get output y (t) as y(t) = 1⁄2 (1 – e-2t) u (t).
5. Is (t)*h(t) = h(t)*x(t)?
a) True
b) False
Explanation: By the properties of convolution we say that x(t)*h(t) = h(t)*x(t)
It can be proved using the convolution integral
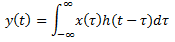
6. Compute u (t) convolved with itself?
a) y(t)=t.u(t)
b) y(t)=u(t)
c) y(t)=t2.u(t)
d) y(t)=t.u(t-1)
Explanation: By taking x (t) = u (t) and h (t) = u (t) and substituting in the integral
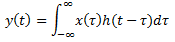
On solving the given integral we get y (t) = t u (t).
7. Convolve the signals e-2t u(t), e-3t u(t). Determine the output?
a) y(t) = (e-2t – e-3t)u(t)
b) y(t) = (e-2t – e-3t)
c) y(t) = (e-3t – e-2t)u(t)
d) y(t) = (e-t – e-3t)u(t)
Explanation: By solving the convolution integral
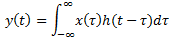
, we get output asy(t) = (e-2t – e-3t)u(t).
8. If two LTI systems with impulse response h1 (t) and h2 (t) and are connected in parallel then output is given by ______
a) y(t) = x(t) *(h1(t) + h2(t))
b) y(t) = x(t) + (h1(t) + h2(t))
c) y(t) = x(t) * (h1(t) h2(t))
d) y(t) = (x(t) * h1(t)) + h2(t)
Explanation: The equivalent impulse response of two systems connected in parallel is the sum of individual impulse responses. It is represented as
y(t) = x(t) * h1(t) + x(t) * h2(t) = x(t) * (h1(t) + h2(t))
9. When two LTI systems with impulse responses ha (t) and hb (t) are cascaded then equivalent response is given by ______
a) h(t) = ha(t) + hb(t)
b) h(t) = ha(t) – hb(t)
c) h(t) = ha(t) hb(t)
d) h(t) = ha(t) * hb(t)
Explanation: The equivalent impulse response of two systems connected in series (cascaded) is given by convolution of individual impulse responses
10. What is this property of impulse response is called ___________
h1(t) * h2(t) = h2(t) * h1(t)
a) Associative property
b) Commutative property
c) Distributive property
d) Closure law
Explanation: Impulse response exhibits commutative property and it is given mathematically by the equation
h1(t) * h2(t) = h2(t) * h1(t).