1. What is the homogenous solution of the system described by the first order difference equation y(n)+ay(n-1)=x(n)? (where ‘c’ is a constant)
a) c(a)-n
b) c(-a)-n
c) c(-a)n
d) c(a)n
Explanation: The assumed solution obtained by assigning x(n)=0 is
yh(n)=λn
=>y(n)+ay(n-1)=0
=>λn+a λn-1=0
=>λn-1(λ+a)=0
=>λ=-a
=>yh(n)=cλn=c(-a)n
2. What is the particular solution of the first order difference equation y(n)+ay(n-1)=x(n) where |a|<1, when the input of the system x(n)=u(n)?
a) \(\frac{1}{1+a}\) u(n)
b) \(\frac{1}{1-a}\) u(n)
c) \(\frac{1}{1+a}\)
d) \(\frac{1}{1-a}\)
Explanation: The assumed solution of the difference equation to the forcing equation x(n), called the particular solution of the difference equation is
yp(n)=Kx(n)=Ku(n) (where K is a scale factor)
=>Ku(n)+aKu(n-1)=u(n)
To determine K we must evaluate the above equation for any n>=1, so that no term vanishes.
=> K+aK=1
=>K=\(\frac{1}{1+a}\)
yp(n)=\(\frac{1}{1+a}\) u(n)
3. If the system is initially relaxed at time n=0 and memory equals to zero, then the response of such state is called as ____________
a) Zero-condition response
b) Zero-state response
c) Zero-input response
d) None of the mentioned
Explanation: The memory of the system, describes, in some case, the ‘state’ of the system, the output of the system is called as zero-state response.
4. The total solution of the difference equation is given as _______________
a) yp(n)-yh(n)
b) yp(n)+yh(n)
c) yh(n)-yp(n)
d) None of the above
Explanation: The linearity property of the linear constant coefficient difference equation allows us to add the homogeneous and particular solution in order to obtain the total solution.
5. Zero-input response is also known as Natural or Free response.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: For a zero-input response, the input is zero and the output of the system is independent of the input of the system. So, the response if such system is also known as Natural or Free response.
6. What is the impulse response of the system described by the second order difference equation y(n)-3y(n-1)-4y(n-2)=x(n)+2x(n-1)?
a) [\(\frac{1}{5}\) (-1)n–\(\frac{6}{5}\) (4)n]u(n)
b) [-\(\frac{1}{5}\) (-1)n–\(\frac{6}{5}\) (4)n]u(n)
c) [\(\frac{1}{5}\) (-1)n+\(\frac{6}{5}\) (4)n]u(n)
d) [-\(\frac{1}{5}\) (-1)n+\(\frac{6}{5}\) (4)n]u(n)
Explanation: The homogenous solution of the given equation is yh(n)=C1(-1)n+C2(4)n—-(1)
To find the impulse response, x(n)=δ(n)
now, for n=0 and n=1 we get
y(0)=1 and
y(1)=3+2=5
From equation (1) we get
y(0)=C1+C2 and
y(1)=-C1+4C2
On solving,
C1=-\(\frac{1}{5}\) and C2=\(\frac{6}{5}\)
=>h(n)= [-\(\frac{1}{5}\) (-1)n + \(\frac{6}{5}\) (4)n]u(n).
7. What is the system does the following direct form structure represents?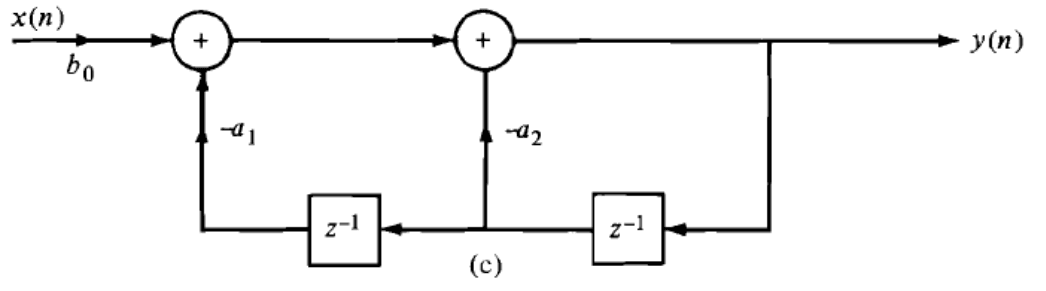
a) FIR system
b) General second order system
c) Purely recursive system
d) None of the mentioned
Explanation: Since the output of the system depends only on the present value of the input and the past values of the output, the system is a purely recursive system.
8. The solution obtained by assuming the input x(n) of the system is zero is ____________
a) Particular solution
b) Homogenous solution
c) General solution
d) Complete solution
Explanation: By making the input x(n)=0 we will get a homogeneous difference equation and the solution of that difference equation is known as Homogenous or Complementary solution.
9. What is the particular solution of the difference equation y(n)=\(\frac{5}{6}y(n-1)-\frac{1}{6}\)y(n-2)+x(n) when the forcing function x(n)=2n, n≥0 and zero elsewhere?
a) \(\frac{8}{5}\) 2n
b) \(\frac{1}{5}\) 2n
c) \(\frac{5}{8}\) 2-n
d) \(\frac{5}{8}\) 2n
Explanation: The assumed solution of the difference equation to the forcing equation x(n), called the particular solution of the difference equation is
yp(n)=Kx(n)=K2nu(n) (where K is a scale factor)
Upon substituting yp(n) into the difference equation, we obtain
K2nu(n)=\(\frac{5}{6}\)K2n-1u(n-1)-\(\frac{1}{6}\) K2n-2u(n-2)+2nu(n)
To determine K we must evaluate the above equation for any n>=2, so that no term vanishes.
=> 4K=\(\frac{5}{6}\)(2K)-\(\frac{1}{6}\) (K)+4
=> K=\(\frac{8}{5}\)
=> yp(n)=(8/5) 2n.
10. What is the zero-input response of the system described by the homogenous second order equation y(n)-3y(n-1)-4y(n-2)=0 if the initial conditions are y(-1)=5 and y(-2)=0?
a) (-1)n+1 + (4)n-2
b) (-1)n+1 + (4)n+2
c) (-1)n-1 + (4)n-2
d) None of the above
Explanation: Given difference equation is y(n)-3y(n-1)-4y(n-2)=0—-(1)
Let y(n)=λn
Substituting y(n) in the given equation
=> λn – 3λn-1 – 4λn-2 = 0
=> λn-2(λ2 – 3λ – 4) = 0
the roots of the above equation are λ=-1,4
Therefore, general form of the solution of the homogenous equation is
yh(n)=C1 λ1n+C2 λ2n
=C1(-1)n+C2(4)n—-(2)
The zero-input response of the system can be calculated from the homogenous solution by evaluating the constants in the above equation, given the initial conditions y(-1) and y(-2).
From the given equation (1)
y(0)=3y(-1)+4y(-2)
y(1)=3y(0)+4y(-1)
=3[3y(-1)+4y(-2)]+4y(-1)
=13y(-1)+12y(-2)
From the equation (2)
y(0)=C1+C2 and
y(1)=C1(-1)+C2(4)=-C1+4C2
By equating these two set of relations,
C1+C2=3y(-1)+4y(-2)=15
-C1+4C2=13y(-1)+12y(-2)=65
On solving the above two equations we get C1=-1 and C2=16
Therefore the zero-input response is Yzi(n) = (-1)n+1 + (4)n+2.