1. If peak voltage of a carrier wave is 10V, what is the peak voltage of modulating signal if modulation index is 50%?
a) 10V
b) 20V
c) 8V
d) 5V
Explanation: From the relation, Modulation Index (µ) = Vm/Vc = 50% = 0.5,
where Vm = Peak voltage of modulating signal,
Vc = Peak voltage of a carrier wave = 10V,
Therefore, Vm = 10 X 0.5 = 5V.
2. Maximum Amplitude of an amplitude modulated 10V and minimum amplitude is 5V. Find its modulation index?
a) 0.65
b) 0.9
c) 0.33
d) 1
Explanation: We know, Modulation Index(µ) = (Vmax-Vmin)/(Vmax+Vmin),
Where, Vmax = Maximum Amplitude of an amplitude modulated = 10V
Vmin = Minimum amplitude of an amplitude modulated = 5V
Therefore, µ = (10-5)/(10+5) = 0.33.
3. 24 channels, each band limited to 3.4 KHz, are to be time division multiplexed. Find the bandwidth required for 128 quantization level? (Given that sampling frequency is 8 KHz)
a) 2436 KHz
b) 1002 KHz
c) 1536 KHz
d) 1337 KHz
Explanation: N = 24, fm = 3.4 kHz
m = 128,
2n = m = 128, n = 7
But fs = 2fm, where, fs = sampling frequency
instead at 2fm 2 x 3.4 kHz 6.8 KHz.
B.W. = N(n+1)X fs = [24(7 + 1)] 8 kHz = 1536 KHz.
4. Sampling frequency of a signal is 6 KHz and is quantized using 7 bit quantizer. Find its bit rate?
a) 42kbPs
b) 64kbPs
c) 16kbPs
d) 8kbPs
Explanation: Bit rate refers to the rate at which data is processed or transferred. It is usually measured in seconds, ranging from bps for smaller values to kbps and mbps.
Bit rate is also known as bitrate or data rate.
Bit rate, Rb = 1⁄Tb where
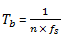 where n = number of bits and fs = Sampling Frequency
where n = number of bits and fs = Sampling FrequencyTb = 1/42, therefore Bit rate = 42 Kbps.
5. Calculate power in each sideband, if power of carrier wave is 96W and there is 40% modulation in amplitude modulated signal?
a) 11.84W
b) 6.84W
c) 3.84W
d) 15.84W
Explanation: Modulation index = 0.4 and Pc = 96W. Power in sidebands may be calculated as
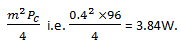
6. For 50% modulation, power in each sideband is ________ of that of carrier.
a) 10%
b) 4.32%
c) 5%
d) 6.25%
Explanation: Modulation index = 0.5. Power in sidebands may be calculated as

7. For 100% modulation, total power is ________
a) 1.5Pc
b) 2Pc
c) 3.75Pc
d) 1.25Pc
Explanation: Total power, Pt = Pc (1 + µ2⁄2), where Pc = Carrier Power
where µ = 1 (for 100% modulation),
so Pt = Pc(1 +(12/2)). On solving it we get Pt = 1.5Pc.
8. If each element of signal occupies 70ms, what will its speed?
a) 11.23 bauds
b) 14.28 bauds
c) 17.39 bauds
d) 13.33 bauds
Explanation: The carrier signal is characterized by the number of signal intervals, or pulses, that are transmitted per second. Each pulse is called a baud. Bps stands for bits per second. Bps is a measure of how many bits can be transmitted during one pulse (one baud).
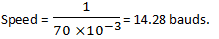
9. Power of carrier wave is 300W and modulation index is 0.75. Find its total power?
a) 465W
b) 384W
c) 323W
d) 502W
Explanation: Total power, Pt = Pc (1 + µ2⁄2), where Pc = Carrier Power = 300W
where Modulation Index (µ) = 0.75,
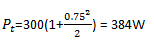
10. If a wave is modulated by two waves. One of them has modulation index equal to 0.75 and other has 0.2, the total modulation index will be ________
a) 0.67
b) 0.58
c) 0.77
d) 0.35
Explanation: Given that m1 = 0.75 and m2 = 0.2. Total modulation index will be equal to
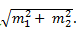 By substituting values we have
By substituting values we have 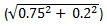 which is equal to 0.77.
which is equal to 0.77.