1. What is the product of following polymerization reaction?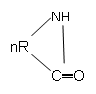
a) ─[─NH─R─CO─]n
b) ─[─R─NH─CO─]n
c) ─[─NH─R─CO─]n-1
d) none of the mentioned
Explanation: The lactam group polymerizes to give ─[─NH─R─CO─]n product, consisting of amide group.
2. What is the order of a self-catalyzed polyesterification reaction?
a) 2
b) 3
c) 1
d) 4
Explanation: For each step of reaction between a –COOH group and –OH group, a second functional group –COOH acts as a catalyst in the reaction. Therefore, the reaction follows the third order kinetics.
3. How is the reactivity of a specific functional group, in general, dependent on the size of the molecule to which it is attached, in a polycondensation reaction?
a) increases with increase in molecular size
b) decreases with decrease in molecular size
c) independent of molecular size
d) cannot be determined
Explanation: The reactivity of functional is independent of the size of the molecule to which it is attached.
4. Which of the following is true about polymer systems in polycondensation?
a) have higher viscosity than small non-polymeric molecules
b) insoluble beyond a critical molecular weight
c) all of the mentioned
d) none of the mentioned
Explanation: The medium viscosity in polymer systems is much higher than the systems of small non-polymeric molecules. Besides, there tend to become insoluble after a certain range of chain length or molecular weight.
5. Which order kinetics does a strong acid catalyzed polyesterification reaction follow?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Explanation: This reaction is achieved by addition of a strong acid catalyst, which is not utilized in the reaction as in self catalyzed reaction. So, the reaction clearly, follows second order kinetics.
6. What is the slope of the line plotted between square of the average degree of polymerization and time for a self catalyzed polyesterification?
a) 2c02k
b) 2c0k
c) c0k/2
d) c02k
Explanation: The rate of disappearance of carboxyl groups is given by, -dc/dt = kc3 (due to self catalyzation, second COOH group acts as catalyst, and reaction follows third order kinetics)
On integration we get,
2kt = 1/c2 – constant
On substituting c=c0(1-p), we get
2c02kt = 1/(1-p)2 – constant
This equation gives the slope equal to 2c02k.
7. What factors may be responsible for deviation in the high conversion region of self-catalyzed polycondensation?
a) loss of reactants
b) cyclization
c) other side reactions
d) all of the mentioned
Explanation: The deviation from linearity in the high conversion region may have arisen due to the factors including loss of reactants, cyclization or other side reactions.
8. What is true about an end functional group, having a terminal reactive centre, of a polymer molecule?
a) has a greater mobility than the polymer molecule as a whole
b) has a lower mobility than the polymer molecule as a whole
c) same as polymer molecule
d) cannot be determined
Explanation: The functional group at a free end has a good degree of mobility to collide and faster reaction to take place.
9. How does the reaction rate vary with increasing extent of reaction beyond 94% conversion in self catalyzed reaction?
a) decreases
b) increases
c) remains same
d) none of the mentioned
Explanation: The reaction rate decreases with increasing extent of reaction beyond 94%. The factors responsible are loss of reactants, difficulty in removal of byproduct molecule due to high viscosity and other side reactions.
10. What is the average degree of polymerization for a complete polycondensation reaction in a bifunctional system?
a) infinity
b) 0
c) 1
d) none of the mentioned
Explanation: For a bifunctional system, average functionality, f=2 and for a complete reaction, extent of reaction, p=1. So the expression for extent of reaction reduces to,
p = [1-(1/Xn)] where, Xn is the average degree of polymerization. Therefore, Xn=∞. Although it is possible only in hypothetical situation.