1. In Fischer–Tropsch process, the particles of the bed are _______
a) Catalysts
b) Coal
c) Silica
d) Stones
Explanation:In Fischer–Tropsch process, Carbon Monoxide and hydrogen are converted to hydrocarbons with metal catalysts as the pellets in fluidised bed. The temperature of operation is about 300℃ and 2-3 atmospheres.
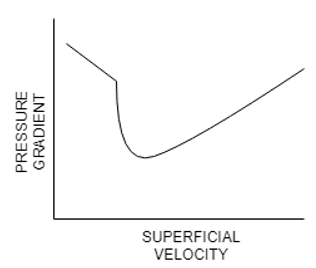
2. Zenz diagram is drawn with the following axis, which one is correct?
a) Pressure drop vs Gas velocity
b) Pressure drop vs superficial velocity
c) Superficial velocity vs pressure drop
d) Pressure drop vs Terminal velocity
Explanation: The Zenz diagram is drawn between the Pressure drop vs superficial velocity.
3. Which one of the following description best suits the definition of slip-stick flow bed?
a) Dilute phase flow
b) Laminar flow
c) Sticky flow
d) Dense phase flow
Explanation:Dense phase non-fluidised solid flow, in which particles move as a block, has been referred to as moving-bed flow, packed bed flow or slip-stick flow. There are usually agitators to monitor the accumulation.
4. After fluidisation, the pressure drop in the fluid phase across the bed is _______ to the bed weight over unit surface of the bed cross section.
a) Equal
b) Slightly more
c) Much greater
d) Less
Explanation:When the upward drag force is equal to the weight of the solids, they become free but not free enough to have random movements inside the fluid, so for fluidisation, upward drag force must be little higher. Hence there is a little extra pressure drop for this reason.
5. When the bed is fluidized with liquids, it is known as ___________ fluidization, and with gas too it is known as ___________ fluidization.
a) Homogeneous, Homogeneous
b) Heterogeneous, Homogeneous
c) Homogeneous, Heterogeneous
d) Heterogeneous, Heterogeneous
Explanation:When fluidised with a liquid, the interaction between solid and liquid is more effective due to the viscosity of the fluids, hence all the pellets are then in complete free fall state as compared to gases when the solids are always partially free. Hence when the bed is fluidized with liquids, it is known as homogeneous fluidization, and with gas it is known as heterogeneous fluidization.
6.The curve in the Zenz – diagram represents ________ as the pressure drop per unit of length as a function of the air flow (or air velocity).
a) Pneumatic conveying
b) Fluidised Reactor
c) Packed bed
d) Shell and Tube heat exchanger
Explanation: The Zenz diagram represented below is the plot of pressure drop versus superficial velocity foe pneumatic conveying specifically.
7. The gas phase fluidised bed is commonly known as ______________ because of its top surface fluidisation.
a) Bubbling fluidized bed
b) Bursting fluidised bed
c) Partially fluidised bed
d) Chaotic fluidised bed
Explanation: When the gas flow velocities are just above the minimum fluidization velocity, bubbles form and the fluidized bed can be treated as if it consists of two phases, a bubbles phase with no particles and a particulate phase. Bubbles which form near the gas inlet, rise up the bed, grow and coalesce, producing bigger bubbles which sometimes break up into smaller bubbles.
8. The pressure drop in bubbling fluidised bed ___________ with time for a given flow velocity.
a) Increases
b) Decreases
c) Oscillates
d) Remains same
Explanation:The pressure drop oscillates with time because the gas inlet is intermittent and the bubbles burst at any moment, hence the pressure drop oscillates.
9. The fluidized state, occurring between the filtration of the fixed bed and the pneumatic conveying regime contains three different regimes. Which one of the following is not correct?
a) Stationary bubbling fluidized bed
b) Dense Flow fluidised bed
c) Fast fluidization
d) Turbulent fluidized bed
Explanation:The fluidized state, occurring between the filtration of the fixed bed and the pneumatic conveying regime contains three different regimes which are collectively known as stationary bubbling fluidized bed, turbulent fluidized bed and the regime of fast fluidization. Dense phase flow is for liquids and highly viscous fluids, never for gases.
10. As the fluidization velocity increases, large bubbles break up into several smaller ones and when this break-up process overcomes the coalescence of the bubbles, oscillations of the pressure drop become smaller. This is the moment when _________ regime occurs.
a) Laminar
b) Mixing
c) Transition
d) Turbulent
Explanation: When the turbulent regime is reached the pressure drop becomes smooth because simultaneously there is a large number of bubbles forming and bursting at the same time which increases the void space and almost equalises the pressure drop