1.The thermal conductivity of the fin should _________ with time.
a) Exponentially increasing
b) Increasing
c) Decreasing
d) Constant
Explanation: The first and the prime assumption we make while deriving equations for Fins is that we assume the heat flow to be in steady state. For the heat flow to be in steady state, the thermal conductivity of the fin material should stay constant. If it changes with time, then the heat transfer rate will also be affected by this change
2. The Heat Transfer Coefficient remains constant throughout the surface of the fin.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: The first and the prime assumption we make while deriving equations for Fins is that we assume the heat flow to be in steady state. For the heat flow to be in steady state, the heat transfer coefficient should stay constant. If it changes with time, then the heat transfer rate will also be affected by this change.
3. Which one of the following is correct about the temperature of the fluid in contact with the fins?
a) Is at a constant temperature
b) Temperature increases along the fin length
c) Temperature decreases along the fin length
d) Depends on flow pattern
Explanation: The first and the prime assumption we make while deriving equations for Fins is that we assume the heat flow to be in steady state. As a consequence of this, the temperature of the fluid in contact with the fins should be at a constant temperature.
4. What is the correct values of X and Y in the following diagram?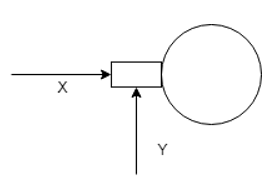
H = Total heat transferred
a) X = H, Y = 0
b) X = 0, Y = H
c) X = H/2, Y = H/2
d) X = H/L, Y = H – H/L
Explanation: It is assumed that the heat transferred across the width of the fin is negligible because of the large length of the fin which absorbs all the heat.
5. By increasing the fin density, the heat transfer coefficient associated with fins__________
a) Decreases
b) Increases
c) Remains the same
d) Increases tenfold
Explanation: There is a limit to which we can apply fins to a surface, if the fin density crosses this threshold value, the heat transfer coefficients decreases as the liquid fails to make proper contact with the provided surface.
6. What is the flow area in the following diagram?
Inner Tube Diameter = 20mm
Outer Tube Diameter = 40mm
Fin width = 5mm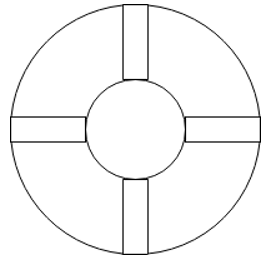
a) 743.5 sq mm
b) 740.5 sq mm
c) 742.5 sq mm
d) 741.5 sq mm
Explanation: We have Total Area, A = π/4 (402 – 202) – 5×10×4 = 742.5 sq mm.
7. Adding fins inside the tube, that is for the tube side usually ________ the heat transfer coefficient.
a) Decreases
b) Increases
c) Tenfold
d) Does not change
Explanation: Usually the tube side contains the cooling liquid and the heat transfer coefficient is already high there, hence adding extra heat transfer area will not be of any help rather would decrease flow rate and eventually decrease the heat transfer coefficient.
8. Which type of fin is not used in Plate-Fin Heat exchangers?
a) Louver
b) Triangular or corrugated
c) Wavy
d) Longitudinal
Explanation: Usually the fins used for Plate Fin heat exchangers are Wavy, Louver and corrugated Fins. Longitudinal fins are not used for plate fins rather for it, needle fins are used if the above three are not available.
9. Recognize the equipment for the following fin.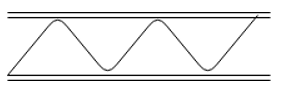
a) Shell and Tube
b) Tube Fin
c) Double Pipe
d) Plate Fin
Explanation: Usually the fins used for Plate Fin heat exchangers are Wavy, Louver and corrugated Fins. The diagram shown above is that of a Corrugated Fin.
10. Tube Fin HE can be classified to two categories which are Conventional and Specialised Tube Fins HE.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: The statement is true because in tube fin HE, there are two possible arrangement, one is conventional where we keep the fins at the gas side and other specialised here we decide fins on the side which has lesser HT coefficient.