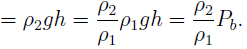1. Which among these devices are the best suited for the measurement of high pressure liquids with high accuracy?
a) Dead Weight Gauge
b) Vacuum Gauge
c) Manganin wire pressure
d) Ionization Gauge
Explanation: Manganin wire is the most suitable measurement device for high pressure liquids. It has a high stability and durability on a long term basis. It also has a high hydrostatic pressure sensitivity and low strain sensitivity.
2. How do we measure the flow rate of liquid?
a) Coriolis method
b) Dead weight method
c) Conveyor method
d) Ionization method
Explanation: Coriolis concept of measurement of fluid takes place through the rotation with the reference frame. It is an application of the Newton’s Law. The device continuously records, regulates and feeds large volume of bulk materials.
3. What is the instrument used for the automatic control scheme during the fluid flow?
a) Rotameters
b) Pulley plates
c) Rotary Piston
d) Pilot Static Tube
Explanation: Pilot static tube is a system that uses an automatic control scheme to detect pressure. It has several holes connected to one side of the device. These outside holes are called as a pressure transducer, which controls the automatic scheme during fluid flow.
4. Define Viscosity?
a) Resistance to flow of an object
b) Resistance to flow of air
c) Resistance to flow of fluid
d) Resistance to flow of heat
Explanation: Viscosity is developed due to the relative motion between two surfaces of fluids at different velocities. It happens due to the shear stress developed on the surface of the fluid.
5. What is the viscosity of water at 30oC?
a) 80.1
b) 0.801
c) 801
d) 0.081
Explanation: A graph is plotted with temperature in the x-axis and dynamic viscosity in the y-axis. With the increase in pressure the viscosity decreases. It corresponds to an informal concept of thickness.
6. Which one of the following is the unit of pressure?
a) N
b) N/m
c) N/m2
d) N/m3
Explanation: Pressure is defined as the force per unit area acting normal to a surface. The SI unit of force is N and area is m2. Thus, the unit of pressure will be N/m2.
7. Which one of the following is the dimension of pressure?
a) [MLT2].
b) [MLT-2].
c) [ML-1T2].
d) [ML-1T-2].
Explanation: Pressure (p) is defined as the force (F) per unit area (A) acting normal to a surface.
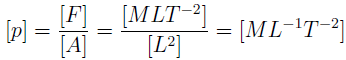
8. Which one of the following statements is true regarding pressure?
a) Pressure is a scalar quantity
b) Pressure is a vector quantity
c) Pressure is a scalar quantity only when the area is infinitesimally small
d) Pressure is a vector quantity only when the area is infinitesimally small
Explanation: Pressure is defined as the force per unit area acting normal to a surface. Both force and area are vectors, but the division of one by the other leads to a scalar quantity.
9. A beaker half-filled with water is exposed to the atmosphere. If the pressure at points A, B and C as shown are Pa, Pb and Pc respectively, which one of the following will be the relation connecting the three?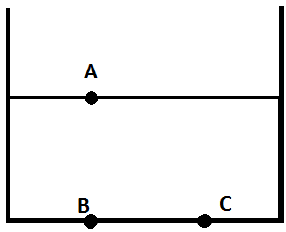
a) Pa > Pb = Pc
b) Pa > Pb > Pc
c) Pa < Pb < Pc
d) Pa < Pb = Pc
Explanation: Since the beaker is exposed to the atmosphere, the pressure at point A will be atmospheric, Pa = 0. Pressure increases in the vertically downward direction, Pa < Pb and Pa < Pc.
Pressure remains constant in the horizontal direction, Pb = Pc. Therefore, Pa < Pb = Pc.
10. A beaker is filled with a liquid of density ρ1 up to a certain height. The pressure at the base of the beaker id Pb. If the liquid is replaced by an equal volume of another liquid of density ρ2, what will be the pressure at the base of the beaker now?
a) Pb
b) \(\frac{ρ1 + ρ2}{2}\) Pb
c) \(\frac{ρ1}{ρ2}\) Pb
d) \(\frac{ρ2}{ρ1}\) Pb
Explanation: PB = ρ1gh, where h=height up to which the liquid is filled. Since equal volume of the second liquid is poured, it’ll also rise to a height of h. Thus, the pressure at the base will become