1. The rise in the level of a liquid in a tube is h. What will be the rise in the level if the same amount of liquid is poured into a tube of half the diameter.
a) 0
b) h/2
c) h
d) 2h
Explanation:
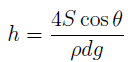
where h = rise in liquid height in the tube, S = surface tension, θ = the angle of contact, d = diameter of the tube, ρ = density of liquid and g = acceleration due to gravity. All other factors remaining constant, h α d. Thus, if d is halved, h will be doubled.
2. The ratio of the surface tension S and density ρ of liquid 1 and 2 are 1:2 and 1:4 respectively. Equal amount of the two liquids is poured into two identical tubes. what will be the ratio of the rise in the liquid level in the two tubes? (Assume the angle of contact to be same)
a) 1:2
b) 2:1
c) 8:1
d) 1:8
Explanation:
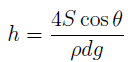
where h = rise in liquid height in the tube, S = surface tension, θ = the angle of contact, d = diameter of the tube, ρ = density of liquid and g = acceleration due to gravity.
Given, S1 / ρ1 = 1 : 2 and S2 / ρ2 = 1 : 4.
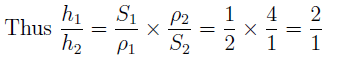
3. The rise in the level of a liquid in a tube is h. If half the amount is poured outside, what will be the new rise in liquid level?
a) 0
b) h/2
c) h
d) 2h
Explanation: The rise in liquid level for a liquid is independent of the amount of liquid present in the tube. Since, same tube is used and same liquid is considered, the rise in the liquid level will remain the same.
4. If a glass tube of 10 mm diameter is immersed in water, what will be the rise or fall in capillary?
(Take surface tension = 0.075 N/m, g = 10 m/s2 and angle of contact = 0)
a) 0.75
b) 1.5
c) 3
d) 6
Explanation:
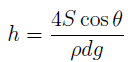
where h = rise in liquid height in the tube, S = surface tension, θ = the angle of contact, d = diameter of the tube, ρ = density of liquid and g = acceleration due to gravity. Substituting all the values,
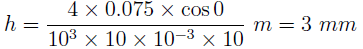
5. A water drop of diameter 1 cm breaks into 1000 similar droplets of same diameter. What will be the gain or loss in the surface energy? (Take surface tension as 0.075 N/m)
a) gain of 0.424 mJ
b) gain of 0.212 mJ
c) loss of 0.212 mJ
d) loss of 0.424 mJ
Explanation: According to the Principle of Conservation of mass, M = 1000 * m, where M = mass of the big drop, m = mass of each droplet. Assuming density to be constant, D3 = 1000 * d3, i.e. D = 10d, where D = diameter of big drop, d = diameter of a droplet.
Change in surface energy = Surface tension * Change in surface area = 0:075*(1000 * πd2 – πD2) = 0:075 * (10 * πD2 – πD2) = 0:075 * 9π * (10-2)2 = 0:212 mJ Since, the change is positive, there will be a gain in the surface energy.
6. If there is no exchange of heat between system and surrounding where system comprises of a compressible fluid but the heat is generated due to friction, the process is an adiabatic.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: For process to be adiabatic, there is no heat exchange and no heat generation within fluid.
7. For a compressible fluid, if there is no change in specific volume at constant temperature, what type of process it is?
a) Isothermal process
b) Adiabatic Process
c) Polytropic process
d) None of the mentioned
Explanation: As, specific volume remains constant, density remains constant. Therefore for given temperature there is no change in volume. hence, the process is isothermal.
8. If the fluid is incompressible, do thermodynamic properties play an important role in its behaviour at varying temperature and pressure?
a) Yes
b) No
c) Depends on the fluid
d) None of the mentioned
Explanation: If fluid is incompressible there is not much change in observed properties with variation in temperature and pressure. Hence, no perceivable change.
9. If for same temperature and pressure change, the value of bulk modulus is compared for isothermal process and adiabatic process, which one would be higher?
a) Isothermal process
b) Adiabatic process
c) Value is constant for both the processes
d) None of the mentioned
Explanation: For isothermal process
K=p
For adiabatic process
K=kp
where K=Bulk modulus
k=Polytropic constant
p=Pressure.
10. The value of gas constant is same for all the gases
a) True
b) False
Explanation: The value of gas constant depends on molecular weight. As the molecular weight is different, gas constant will be different.