1. When the acceleration of the piston is 0, then the velocity is _____
a) Maximum
b) Minimumn
c) Negative
d) Half the maximum
Explanation: When the crank and the connecting rod are perpendicular to each other, at that instance the acceleration is 0 but the velocity is maximum.
2. If OC is the crank and PC is the connecting rod of a reciprocating steam engine and rotates with uniform angular velocity in clockwise direction in the given figure below: then under which condition the piston will undergo retardation?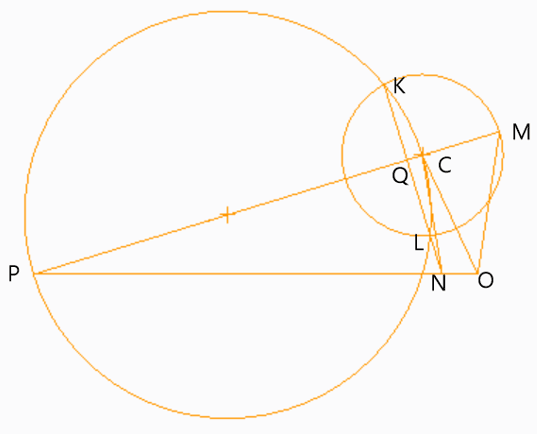
a) N lies to the right of O
b) N lies to the left of O
c) N is above O
d) N is below O
Explanation: The point N has to remain in the horizontal line of OP thus both the options of N being above O and N being below are incorrect. When N lies to the left of O the piston undergoes acceleration.
3. In the given figure, the velocity of piston is maximum under which of the following conditions?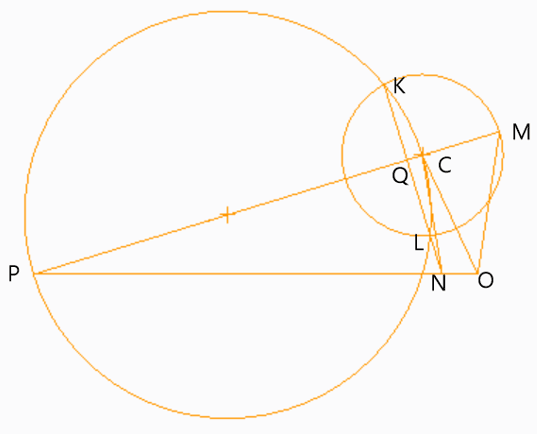
a) N lies to the left of O
b) N lies to the right of O
c) N coincides with O
d) N lies above O
Explanation: When the crank and the connecting rod are perpendicular to each other, at that instance the acceleration is 0 but the velocity is maximum.
4. With respect to the figure given quadrilateral CQNO is known as _______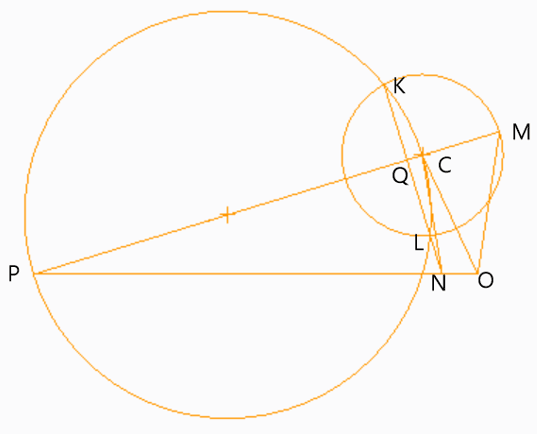
a) Klein’s acceleration diagram
b) Klein’s velocity diagram
c) Klein’s displacement diagram
d) Bennet’s diagram
Explanation: Ar(co) is parallel to CO, Ar(cp) is parallel to CP, At(pc) is parallel to QN and Apo is parallel to PO thus quadrilateral CQNO is the acceleration polygon
5. A Piston will remain in equilibrium if ________
a) Inertia force is applied in the same direction to the resultant force
b) Inertia force is applied in the direction opposite to the resultant force
c) Inertia force is applied in the direction Perpendicular to the resultant force
d) Inertia force is applied in the direction Parallel to the resultant force
Explanation: Inertia force is an imaginary force which tends to act in the direction opposite to the resultant force to bring the body in equilibrium. The magnitude of this force is equal to that of resultant force.
6. Klein’s constructions can be used to determine the acceleration of various parts at all locations
a) True
b) False
Explanation: Klein’s constructions provide acceleration diagram of the entire mechanism through which the acceleration of various parts can be calculated.
7. For a slider crank mechanism, the total no. of dead centres are ____
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Explanation: Dead centres are locations where the velocity of the piston is 0, hence there are only two locations where this is possible in the slider crank mechanism
8. Klein’s construction gives a graphical construction of a 4 bar chain
a) True
b) False
Explanation: Klein’s construction is used to draw the graphical construction of acceleration and velocity polygon of a slider crank mechanism.
9. If OC is the crank and PC is the connecting rod rotating in clockwise direction in the figure given below, then triangle OCM is known as ________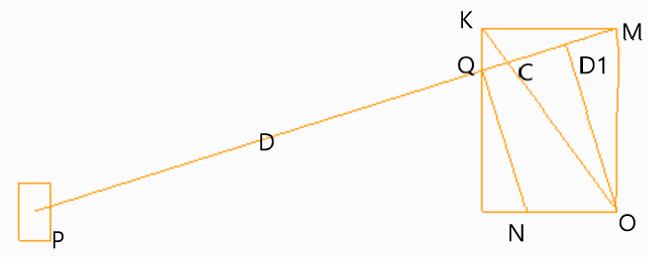
a) Klein’s velocity diagram
b) Klein’s acceleration diagram
c) Ritterhaus’ velocity diagram
d) Ritterhaus’ acceleration diagram
Explanation: Since the crank is rotating in the clockwise direction, then the velocity of C will be perpendicular to OC and it’s value is given by w2.OC, hence triangle OCM forms a velocity polygon
10. Ritterhaus’ construction is used when the motion of the crank is linear shm.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: Ritterhaus’ construction is used when the crank is undergoing a motion which has uniform angular velocity.