1. What happens when the amplitude of the modulating signal is greater than the amplitude of the carrier?
a) Decay
b) Distortion
c) Amplification
d) Attenuation
Explanation: The zero reference line of the modulating signal coincides with the peak value of the unmodulated carrier. Because of this, the relative amplitudes of the carrier and modulating signal are important. When the amplitude of the modulating signal is greater than the amplitude of the carrier, distortion will occur.
2. What is the effect of distortion?
a) Total information loss
b) Error information
c) Attenuated information
d) Amplified information
Explanation: Distortion occurs when the modulating signal amplitude is greater than the amplitude of the carrier, causing incorrect information to be transmitted. In amplitude modulation, it is particularly important that the peak value of the modulating signal be less than the peak value of the carrier.
3. What is the circuit used for producing AM called?
a) Modulator
b) Transmitter
c) Receiver
d) Duplexer
Explanation: The circuit used for producing AM is called a modulator. It has two inputs, the carrier and the modulating signal, and the resulting output is the modulated signal. Amplitude modulators compute the product of the carrier and modulating signals.
4.What is the percentage of modulation if the modulating signal is of 7.5V and carrier is of 9V?
a) 100
b) 91
c) 83.33
d) 0
Explanation: modulation index m = Vm⁄Vc = 7.5⁄9* 100 = 83.33.
5. When does over-modulation occur?
a) Modulating signal voltage < Carrier voltage
b) Modulating signal voltage > Carrier voltage
c) Modulating signal voltage = Carrier voltage
d) Modulating signal voltage =0
Explanation: Over-modulation is a condition in which the modulating signal voltage is much greater than the carrier voltage. The received signal will produce an output waveform in the shape of the envelope, whose negative peaks have been clipped off.
6. What is the condition for greatest output power at the transmitter without distortion?
a) Modulating signal voltage > Carrier voltage
b) Modulating signal voltage < Carrier voltage
c) Modulating signal voltage = Carrier voltage
d) Modulating signal voltage = 0
Explanation: When the modulation index is 1 or the percentage of modulation is 100, modulating signal voltage is equal to the carrier voltage. This results in the greatest output power at the transmitter and the greatest output voltage at the receiver, with no distortion.
7. Which of the following modulating signal voltage would cause over-modulation on a carrier voltage of 10v?
a) 9.5
b) 9.99
c) 10
d) 12
Explanation: When the voltage of the modulating signal exceeds the voltage of the carrier signal over-modulating occurs. Here, 12/10 = 1.2 which is greater than 1 and hence would cause over-modulation.
8. What is the modulating signal voltage if the maximum and the minimum voltages on the wave was observed to be 5.9v and 1.2v respectively?
a) 2.35v
b) 2.12v
c) 1.85v
d) 3.21v
Explanation:
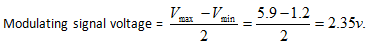
9.What is the wave of frequency that occurs at the sum and difference of the carrier and modulating signal is called?
a) Noise signals
b) Sideband
c) Extraband
d) Neutral band
Explanation: New signals at different frequencies are formed when an intelligence signal is modulated with a carrier. These signals are called sidebands and usually have the frequency of the sum and the difference of the carrier and the modulating signal.
10. What type of display will give us clear information on the signal if it is made up of different frequencies?
a) Frequency domain display
b) Amplitude domain display
c) Time domain display
d) Bandwidth display
Explanation: When a waveform is made up of waves of different frequencies the amplitude information is not enough to fully understand the wave and its propagation characteristics. In this case, a frequency domain display is used where the frequency of each separate signal is shown according to its frequency and amplitude with respect to time.