1. What is the frequency of 7th harmonic of a 2KHz sine wave?
a) 14Khz
b) 9KHz
c) 5KHz
d) 2KHz
Explanation: The frequency of 7th harmonic sine wave = 7 x 2KHz = 14KHz.
2. An infinite number of odd harmonics are present in a sine wave.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: A square wave is made up of a sine wave at the fundamental frequency of the square wave plus an infinite number of odd harmonics. For example, if the fundamental frequency of the square wave is 1 kHz, the square wave can be synthesized by adding the 1-kHz sine wave and harmonic sine waves of 3 kHz, 5 kHz, 7 kHz, 9 kHz, etc.
3. What is the peak value of 5th harmonic if the square wave has a peak voltage of 3v and a frequency of 48Khz?
a) 0.74
b) 0.52
c) 0.76
d) 1.5
Explanation:
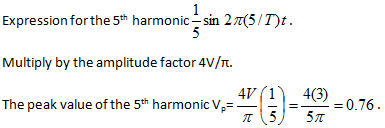
4. Which instrument produces frequency domain information?
a) Oscilloscope
b) Spectrum analyzer
c) Frequency divider
d) Beam analyzer
Explanation: The test instrument for producing a frequency-domain display is the spectrum analyzer. Like the oscilloscope, the spectrum analyzer uses a cathode-ray tube for display, but the horizontal sweep axis is calibrated in hertz and the vertical axis is calibrated in volts or power units or decibels.
5. What is the band width required to pass a signal with t0=75×10-9 without excessive distortions?
a) 14MHz
b) 53.7MHz
c) 13.33MHz
d) 11.56MHz
Explanation:
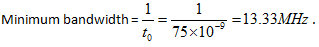
6. A pulse train has a rise time of 6 ns. What is the minimum bandwidth to pass this pulse train faithfully?
a) 58.3MHz
b) 42.6MHz
c) 812MHz
d) 41.5MHz
Explanation:
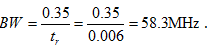
7. A circuit has a bandwidth of 200 kHz. What is the fastest rise time this circuit will pass?
a) 1.5μs
b) 2.3μs
c) 1.2μs
d) 1.75μs
Explanation:
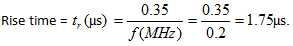
8. Fourier analysis helps us to determine how much bandwidth a particular signal occupies.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: Fourier analysis allows us to determine not only the sine wave components in any complex signal but also how much bandwidth a particular signal occupies. Although a sine or cosine wave at a single frequency theoretically occupies no bandwidth, complex signals obviously take up more spectrum space.
9. What is the line connecting the positive and negative peaks of the carrier waveform called?
a) Peak line
b) Maximum amplitude ceiling
c) Modulation index
d) Envelope
Explanation: An imaginary line connecting the positive peaks and negative peaks of the carrier waveform gives the exact shape of the modulating information signal. This line is known as the envelope.
10. What is the reference line for the modulating signal?
a) Zero line
b) Carrier peak line
c) Modulated peak line
d) Un-modulated peak line
Explanation: The modulating signal uses the peak value of the carrier rather than zero as its reference point. The envelope varies above and below the peak carrier amplitude. The zero reference line of the modulating signal coincides with the peak value of the unmodulated carrier.