1. Function of zinc is
a) Synthesis of chlorophyll
b) Biosynthesis of IAA
c) Closing of stomata
d) Oxidation of carbohydrate
Explanation: Function of zinc is biosynthesis of IAA.
2. The process by which minerals are absorbed is
a) Active absorption
b) Passive absorption
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
Explanation: Both (a) and (b)
3. The active uptake of minerals by roots mainly depends on the
a) Availability of oxygen
b) Light
c) Temperature
d) Availability of carbon dioxide
Explanation: The active uptake of minerals by roots mainly depends on the availability of oxygen.
4. Identify A to D in the given figure.
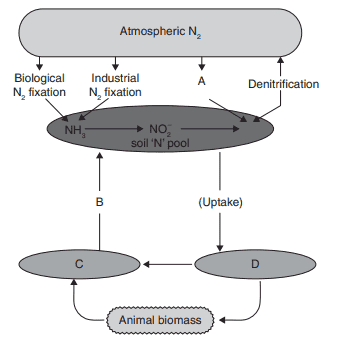
a) A–Decaying biomass, B–Electrical \[N_{2}\] fixation, C–Plant biomass, D–Ammonification
b) A–Plant biomass, B–Decaying biomass, C–Ammonification, D–Electrical \[N_{2}\] fixation
c) A–Electrical \[N_{2}\] fixation, B–Ammonification, C–Decaying biomass, D–Plant biomass
d) A–Ammonification, B–Plant biomass, C–Electrical \[N_{2}\] fixation, D–Decaying biomass
Explanation: A–Electrical \[N_{2}\] fixation, B–Ammonification, C–Decaying biomass, D–Plant biomass
5. Nitrogen is a component of
a) Protein
b) Chlorophyll
c) Nucleic acid
d) All of these
Explanation: All of these
6. Which one of the following can fix atmospheric nitrogen directly?
a) Pea
b) Brassica
c) Castor
d) Petunia
Explanation: Pea can fix atmospheric nitrogen directly
7. Knot like bodies known as ‘nodules’ are found in the roots of groundnut plant it is produced
by
a) Azospirillum
b) Azotobacter
c) Pseudomonas
d) Rhizobium
Explanation: Rhizobium
8.Nitrogen fixation means
a) \[N_{2}\] changes in \[NO_3^-\]
b) \[N_{2}\] changes in \[NH_{3}\]
c) \[N_{2}\] change into nitrates
d) none of these
Explanation: Nitrogen fixation means \[N_{2}\] changes in \[NH_{3}\]
9. Nif genes occur in
a) Rhizobium
b) Aspergillus
c) Penicillium
d) Streptococcus
Explanation: Nif genes occur in Rhizobium.
10. Identify A to C in the given figure.
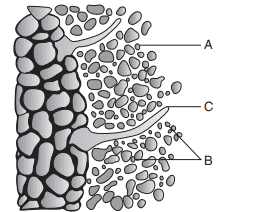
a) A–Bacteria, B–Root hair, C–Soil particles
b) A–Root hair, B–Bacteria, C–Soil particles
c) A–Root hair, B–Soil particles, C–Bacteria
d) A–Soil particles, B–Bacteria, C–Root hair
Explanation: A–Soil particles, B–Bacteria, C–Root hair