1. Equilibrium equations used to analyse cable is _____
a) ∑H = 0 only
b) ∑H = 0 and ∑V = 0 only
c) ∑H = 0, ∑V = 0 and ∑M = 0
d) ∑V = 0 only
Explanation: To analyse the frame completely, we are required with all the three of equilibrium equations i.e. ∑H = 0, ∑V = 0 and ∑M = 0.
2. An arch is a beam except for ____
a) It does not resist inclined load
b) It does not resist transverse forces
c) It does not allow rotation at any point
d) It does not allow horizontal movement
Explanation: An arch is a curved member in which horizontal displacements are prevented at the supports/springings/abutments.
3. An arch is more economical than a beam for a shorter span length.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: Bending Moment for an arch is given by the bending moment produced in simply supported for same loading minus bending moment produced due to horizontal thrust. Since the bending moment produced is lower for the same loading, it is more economical than the beam.
4. Two hinged arches is a determinate structure.
a) True
b) False
Explanation: Two hinged arches is an indeterminate structure. We can calculate vertical reactions by using ∑M = 0 and ∑V = 0 but the horizontal reaction cannot be computed by any of equilibrium equations. Thus, two hinged arches is an indeterminate structure.
5. Calculate the horizontal thrust for the two hinged parabolic arch loaded uniformly throughout with distributed load.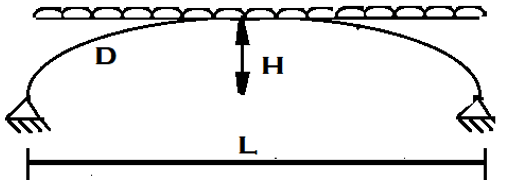
a) \(\frac{WL^2}{32H} \)
b) \(\frac{WL^2}{16H} \)
c) \(\frac{WL^2}{8H} \)
d) \(\frac{WL^2}{2H} \)
Explanation: ∑H = 0
H = \(\frac{∫M.y dy}{∫y^2 dy}\)
Where, y=\(\frac{4 H x ( L-x )}{L^2}\)
Hence, H = \(\frac{WL^2}{8H} \)
6. Calculate the horizontal thrust for the two hinged semicircular arch loaded uniformly throughout with distributed load.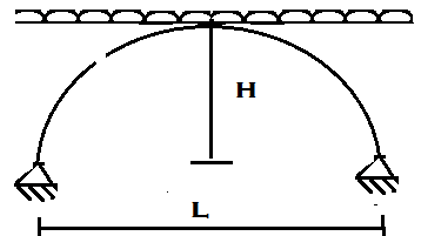
a) \(\frac{W}{\pi}\)
b) \(\frac{W}{\pi}\) sin2∞
c) \(\frac{4RW}{3\pi}\)
d) \(\frac{W}{2\pi}\)
Explanation: ∑H = 0
H = \(\frac{∫M.y dy}{∫y^2 dy}\)
Y = \(\sqrt{R^2- x^2} – \sqrt{R^2-(\frac{L^2}{2})} \)
Hence, H = \(\frac{4RW}{3\pi}.\)
7. Calculate the horizontal thrust for the two hinged semicircular arch loaded with point load at its crown.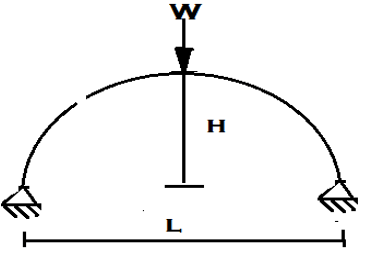
a) \(\frac{W}{\pi}\)
b) \(\frac{W}{\pi}\) 2∞
c) \(\frac{4RW}{3\pi}\)
d) \(\frac{W}{2\pi}\)
Explanation: ∑H = 0
H = \(\frac{∫M.y dy}{∫y^2 dy}\)
Y = \(\sqrt{R^2- x^2} – \sqrt{R^2-(\frac{L^2}{2})} \)
Hence, H = \(\frac{W}{\pi}\)
8. Calculate the horizontal thrust for the two hinged semicircular arch loaded with point load at inclination of α with horizontal axis on the left span.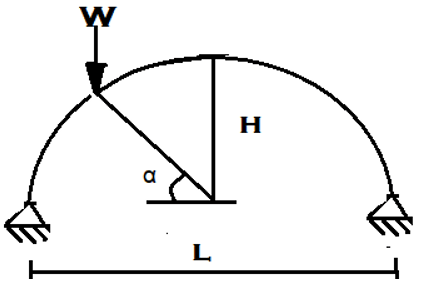
a) \(\frac{W}{\pi}\)
b) \(\frac{W}{\pi}\)sin2∞
c) \(\frac{4RW}{3\pi}\)
d) \(\frac{25WL}{128H}\)
Explanation: ∑H = 0
H = \(\frac{∫M.y dy}{∫y^2 dy}\)
Y = \(\sqrt{R^2- x^2} – \sqrt{R^2-(\frac{L}{2^2})} \)
Hence, H = \(\frac{W}{\pi}\)sin2∞.
9. Identify the incorrect statement according to the hinged arches.
a) Three hinged arch is a statically determinate structure
b) To analyze three hinged arch, equlibrium equations are sufficient
c) For three hinged parabolic arch subjected to u.d.l over the entire span, the bending moment is constant throughout the span
d) For two hinged parabolic arch subjected to u.d.l over the entire span, the bending moment is zero throughout the span
Explanation: For three hinged parabolic arch subjected to u.d.l over the entire span, the bending moment and radial shear at any section is zero throughout the span.
10. In BMD and SFD :-
a) Points remain fixed, position of load changes
b) Points change, position of loads remain fixed
c) Both of them changes
d) Neither of them changes
Explanation: In BMD and SFD, we analyze the structure by fixing loads initially.