1. The tensile stresses developed in steel by the expansion of concrete are about ___________
a) 850n/mm2
b) 250n/mm2
c) 600n/mm2
d) 500n/mm2
Explanation: Tensile stresses of up to 850n/mm2 were developed in steel by the expansion concrete results of laboratory investigations of several types of chemically pre stressed elements, such as beams, slabs, frames, columns, pipes and hyperbolic parabolic sheets have demonstrated the feasibility of chemical pre stressing.
2. The chemical pre stressing is generally suited for elements like ___________
a) Pre cast beams and columns
b) Bonding elements
c) Breakage elements
d) Tensioning elements
Explanation: It has been found that structural elements ideally suited for chemical pre stressing include pipes, thin walls and slabs, shells; folded plates and composite columns as well as pre cast beams and columns.
3. The method of chemical pre stressing is not suited for ___________
a) High degrees of prestress
b) High degrees of compression
c) High degrees of anchoring
d) High degrees of jacking
Explanation: In the present state of art, chemical pre stressing can be applied to structural elements and systems in which the optimum amount of pre stress is relatively low and this method is most not suited for high degrees of prestress and high percentages of steel where mechanical pre stressing can be conveniently used.
4. The suitability of post tensioning is good for ___________
a) Long spans
b) Break spans
c) Edge spans
d) End spans
Explanation: The suitability of post tensioning is good for medium to long span in situ work, where the cost of tensioning is very less and the major advantage of is the stopped off and curved cables are allowed by which designer can easily differ the prestresss distribution.
5. The long span decks are fabricated by ___________
a) Post tensioning
b) Pre tensioning
c) Thermo electric prestress
d) Chemical prestress
Explanation: Post tensioning is ideally suited in concrete construction work involving stage prestressing most of the long span bridge structures are constructed using post tensioning system and long span bridge decks are also fabricated by the use of post tensioning.
6. The concrete dams are constructed using which?
a) Post tensioning
b) Thermo electric pre tensioning
c) Biological pre tensioning
d) Elongation pre tensioning
Explanation: Concrete dams, biological shields of nuclear reactors and circular pre stressing of large concrete tanks are strengthened by using post tensioning and high tensile wire is wrapped under high tension using a wire serving machine developed by the inventors.
7. The resultant stresses in concrete at any section are obtained by the effect of ___________
a) Prestress and flexural stresses
b) Prestress and bending stresses
c) Prestress and shear stresses
d) Prestress and torsion stresses
Explanation: Resultant stresses in concrete at any section are obtained by superimposing the effect of prestress and flexural stresses developed due to the loads, other common types of corrosion frequently encountered in prestressed concrete construction are pitting corrosion and chloride corrosion, a critical review of the different types of corrosion of high tensile steel in structural concrete is reported.
8. The resultant stress distribution due to eccentric prestressing, dead and live loads at any given section are obtained as ___________
a) Fsup = (p/a-pe/zt)+(mg/zt)+(mq/zt)
b) Fsup = (p/a-pe/zt)+(mg/zt)+(mq/zt)
c) Fsup = (p/a-pe/zt)+(mg/zt)+(mq/zt)
d) Fsup = (p/a-pe/zt)+(mg/zt)+(mq/zt)
Explanation: If Mq and Mg are live loads and dead load moments at the central span section;
Mq=ql2/8
Mg=gl2/8
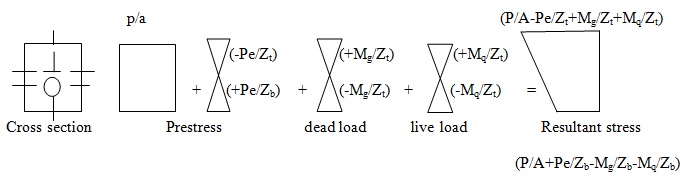
9. A concrete beam of rectangular section, 250mm wide and 600mm deep. Calculate the bending moment that can be applied without applying tension at the soffit of the beam with given m/z value as 5.74?
a) 26.4
b) 54.8
c) 34.5
d) 86.1
Explanation: m/z = 5.74, b = 250mm, d = 600mm
Z = (250×6002/6) = 15×106mm3,
M = (5.74×15×106) = 86.1×106nmm = 86.1knm.
10. A prestressed concrete beam of section 200mm wide by 300mm deep of imposed load 4kn/m at a span of 6m, density of concrete is 24kn/m3. Find the concentric prestressing force necessary for zero fiber stress at the soffit?
a) 490
b) 560
c) 230
d) 310
Explanation: b = 200mm, d = 300mm, A = (200×300) = 6×104mm2, g = (0.2×0.3×24),
Mg = (0.125×1.44×62) = 6.48knm, Mq = (0.125×4×62) = 18knm, Zb=Zt = (200×3002/6) = 3×106mm3
P/A = 8.16, P = (8.16×6×104) = 489.6kn.