1. The locus of the point of contact on two mating teeth from beginning of engagement to end of engagement is known as the _______________
a) angle of action
b) arc of contact
c) path of contact
d) line of action
Explanation: Path of contact is the locus of the point of contact on two mating teeth from beginning of engagement to end of engagement. It is also called as contact length. It is the tangent to both the base circles and passes through the pitch point.
2. The portion of path of contact from the beginning of contact to the pitch point is called _______
a) arc of recess
b) arc of approach
c) path of recess
d) path of approach
Explanation: Path of approach is the portion of path of contact from the beginning of contact to the pitch point. It is given by the formula (Ra2 – R2cos2 φ)0.5 – Rsinφ; where Ra is the radius of addendum of the larger gear, R is the radius of the larger gear and φ is the pressure angle between the two gears.
3. The portion of the path of contact from the pitch point to the end of contact is called _________
a) arc of recess
b) arc of approach
c) path of recess
d) path of approach
Explanation: Path of recess is the portion of the path of contact from the pitch point to the end of contact. It is given by the formula (ra2 – r2cos2 φ)0.5 – rsinφ; where ra is the radius of addendum of the smaller gear, r is the radius of the smaller gear and φ is the pressure angle between the two gears. Path of approach + Path of recess = Path of contact.
4. Arc of contact = ___________________ Complete the equation.
a) Path of contact / cos θ
b) Path of contact / sin θ
c) Path of contact x cos θ
d) Path of contact x sin θ
Explanation: Arc of contact = Path of contact / cos θ; θ = the pressure angle between the two gears
5. The locus of a point on the pitch circle from the beginning to end of engagement of two mating gears is called as ___________
a) Arc of contact
b) Path of contact
c) Path of approach
d) Arc of approach
Explanation: Arc of contact is defined as the locus of a point on the pitch circle from beginning to end of engagement of two mating gears. It is subdivided into two sections namely arc of approach and arc of recess. Arc of approach + arc of recess = arc of contact.
6. The ratio of angle of action to the pitch angle is called ___________
a) space width
b) angle of recess
c) angle of approach
d) contact ratio
Explanation: Contact ratio is the ratio of angle of action to the pitch angle. It is also defined as the number of pairs of teeth in contact. Contact ratio = arc of contact / circular pitch
7. The angle turned by the gear from the beginning to the end of engagement of a pair of teeth is called ______________
a) angle of approach
b) angle of recess
c) angle of action
d) angle of contact
Explanation: Angle of action is the angle turned by the gear from the beginning to the end of engagement of a pair of teeth. Angle of action = Arc of contact / r; where r is the radius of the pinion.
8. In the given diagram identify the path of contact.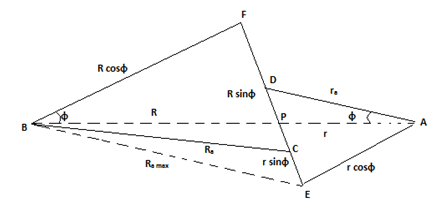
a) CD
b) AB
c) FE
d) BP
Explanation: Path of contact is the locus of the point of contact on two mating teeth from the beginning of engagement to the end of it. Thus CD is the path of contact. It is also called as contact length. It is the tangent to both the base circles and passes through the pitch point.
9. The formula to calculate path of contact is ______________________
a) (Ra2 + R2cos2 φ)0.5 + (ra2 + r2cos2 φ)0.5 – (R+r)sin φ
b) (Ra2 – R2cos2 φ)0.5 + (ra2 – r2cos2 φ)0.5 + (R+r)sin φ
c) (Ra2 – R2cos2 φ)0.5 + (ra2 – r2cos2 φ)0.5 – (R+r)sin φ
d) (Ra2 – R2cos2 φ)0.5 + (ra2 – r2cos2 φ)0.5 – (R-r)sin φ
Explanation:
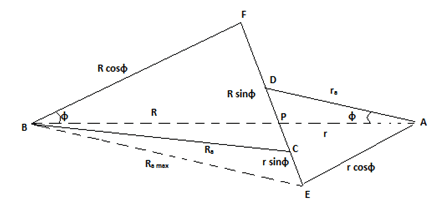
From the diagram of two gears in a mesh, we can clearly see that, CD = CP + PD = (CF – PF) + (DE – PE) =(Ra2 – R2cos2 φ)0.5 + (ra2 – r2cos2 φ)0.5 – (R+r)sin φ.
10.The condition which must be fulfilled by two gear tooth profiles to maintain a constant angular velocity ratio between them is called __________________
a) arc of contact
b) path of contact
c) law of gearing
d) interference
Explanation: Law of gearing is the condition which must be fulfilled by two gear tooth profiles to maintain a constant angular velocity ratio between them. In order to maintain this constant angular velocity, the common normal of the tooth profiles should always pass through a fixed point on the line of centres, called fixed point